Figure 2.
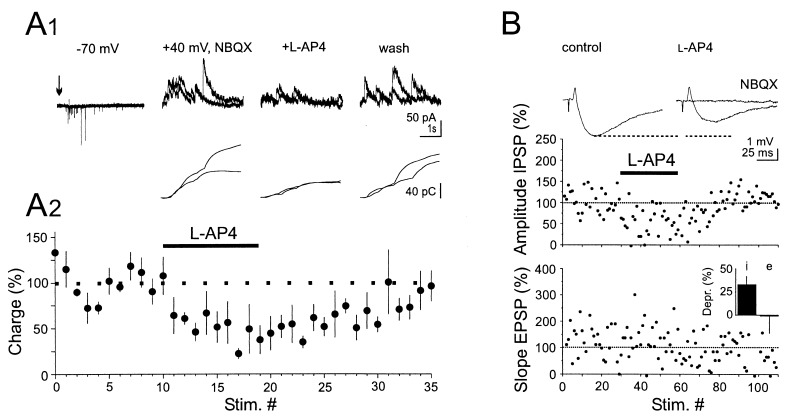
(A) Synaptic transmission at Schaffer collateral/interneuron synapses is decreased by L-AP4. (A1) Potassium puffs (2 × 75 ms, 50 ms interval, arrow) applied every 30 s to the surface of the CA3 stratum pyramidale evoked a burst of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxalozolepropionic acid receptor-mediated EPSCs in a CA1 interneuron voltage- clamped at −70 mV. After bath-application of NBQX (10 μM) the neuron was voltage clamped at +40 mV to record NMDAR-mediated EPSCs. Application of L-AP4 (15 μM) reversibly reduced NMDAR-mediated EPSCs. The current traces are composed of two superimposed sweeps. Lower traces: charge transfer of the current traces illustrated above. (A2). Summary graph of four similar experiments. (B) L-AP4 reduces feed-forward inhibition. Threshold extracellular stimulation in CA3 evoked an EPSP-IPSP sequence in a CA1 pyramidal cell recorded in current-clamp mode (membrane potential manually clamped at −55 mV). The voltage traces represent the average of 20 sweeps. L-AP4 (50 μM) reduced the amplitude of IPSPs but not the slope of EPSPs. Note that NBQX (10 μM) abolished the EPSP and the IPSP. (Inset) Comparison of the action of L-AP4 on IPSPs (i) and EPSPs (e) for the four experiments where a depression of the IPSP was observed.