Fig. 2.
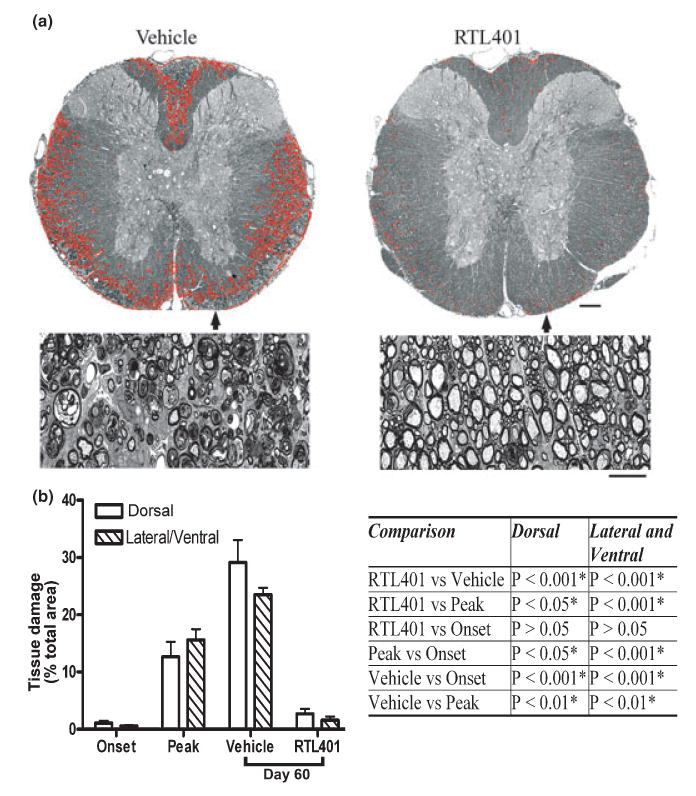
RTL treatment ameliorated tissue (myelin) damage in EAE. (a) Representative thoracic spinal cord sections from vehicle (left panel) or RTL401 (right panel)-treated mice stained with toluidine blue for myelin on day 60 of EAE. (b) Morphometric analysis of the development of myelin damage in the white matter of thoracic spinal cords of EAE treated with vehicle or RTL401. The cords were dissected from paraformaldehyde (PFA) plus glutaraldehyde-perfused EAE mice (4 mice randomly chosen from a group of 8, the rest were euthanized by perfusion with PBS, see Figs 3,4 and 5) euthanized at disease onset (day 11, disease score 1.5), peak (between day 15 and day 20 when the disease score for each mouse reached 4.5), or at the termination of the experiment (day 60 of EAE, after RTL401 or vehicle treatment). Tissue sections were stained with toluidine blue and images were captured with a compound microscope equipped with a digital camera. Areas with tissue damage were measured and analyzed using BIOQUANT classic 95 software. Scale bars = 25 μM (low power views) or 100 μM (high power views). Inserted Table: RTL401-treated mice show a significant reduction in spinal cord white matter tissue damage, demonstrated by one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Kuels multiple comparisons test. *Comparison statistically significant.
