Fig. 3.
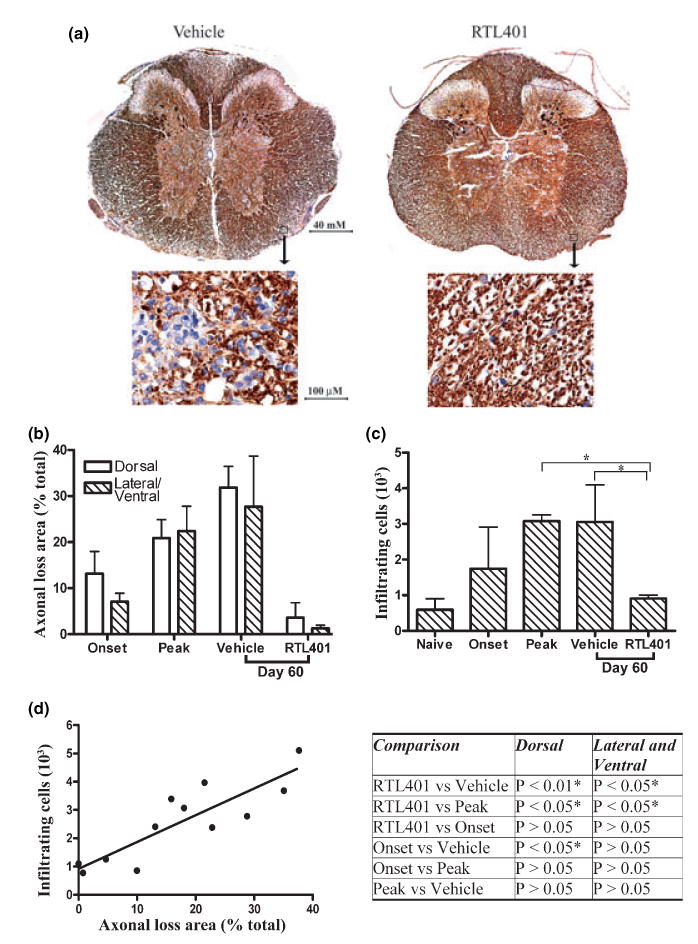
RTL401-treatment decreased axonal loss and inflammation in the spinal cord in EAE. (a) Representative phosphorylated neuro-filament staining of axons in thoracic spinal cord sections from EAE mice treated with vehicle (left panel) or RTL401 (right panel) 60 days after disease induction. Tissue sections were dissected from PBS-perfused mice (4 available mice from a group of eight after 4 randomly chosen mice were perfused by PFA, see Fig. 2), fixed and stained with SMI312, an antibody cocktail for neurofilaments (brown). The nuclei of inflammatory mononuclear cells were visualized by hematoxylin (blue). Images were captured with a compound microscope equipped with a digital camera. (b) Morphometric analysis of the development of axonal loss in EAE mice treated with vehicle or RTL401. EAE mice were euthanized at disease onset (day 11, disease score 1.5), peak (between day 15 and day 20, when disease scores reached 4.5), or at the termination of the experiment (day 60 of EAE, after RTL401 or vehicle treatment). Digitally acquired images were analyzed with BIOQUANT software. Areas with loss of phosphorylated NF staining of axons were circled by hand and traced by BIOQUANT. The percentage of axonal loss area was calculated by dividing total axonal loss areas by the total area of dorsal or lateral/ventral white matter. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 4). (c) RTL401-treatment reduced inflammatory mononuclear cells in the CNS of EAE mice. Total numbers of inflammatory mononuclear cells (stained blue with hematoxylin) in whole thoracic spinal cord sections were counted manually. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 4). *Comparison statistically significant as demonstrated by one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Kuels multiple comparisons test, n = 4. (d) Correlation of axonal loss to number of inflammatory cells in individual mice. Pearson’s correlation analysis showed a significant correlation, r = 0.8636, p (two-tailed) = 0.0003. Inserted Table: RTL401-treated mice show a significant reduction in axonal loss, demonstrated by one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Kuels multiple comparisons test. *Comparison statistically significant.
