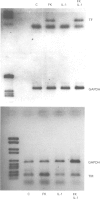
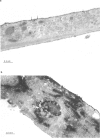
Abstract
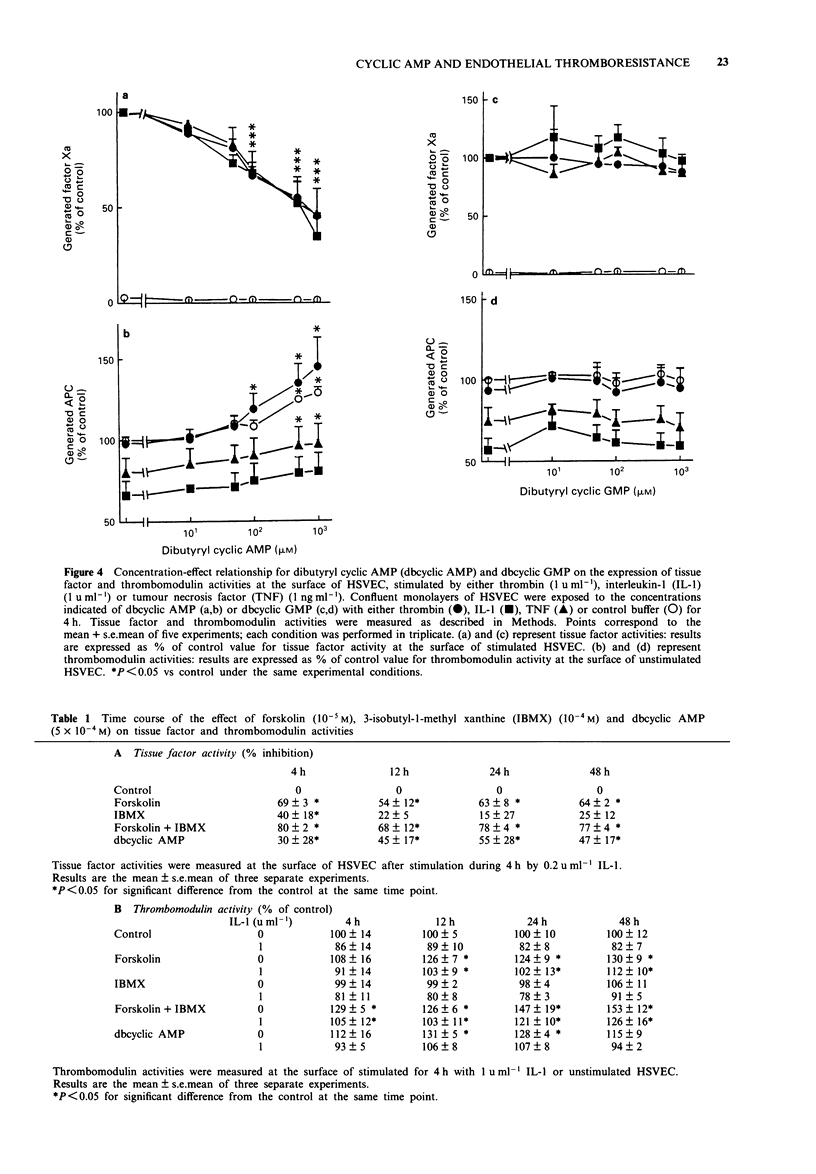
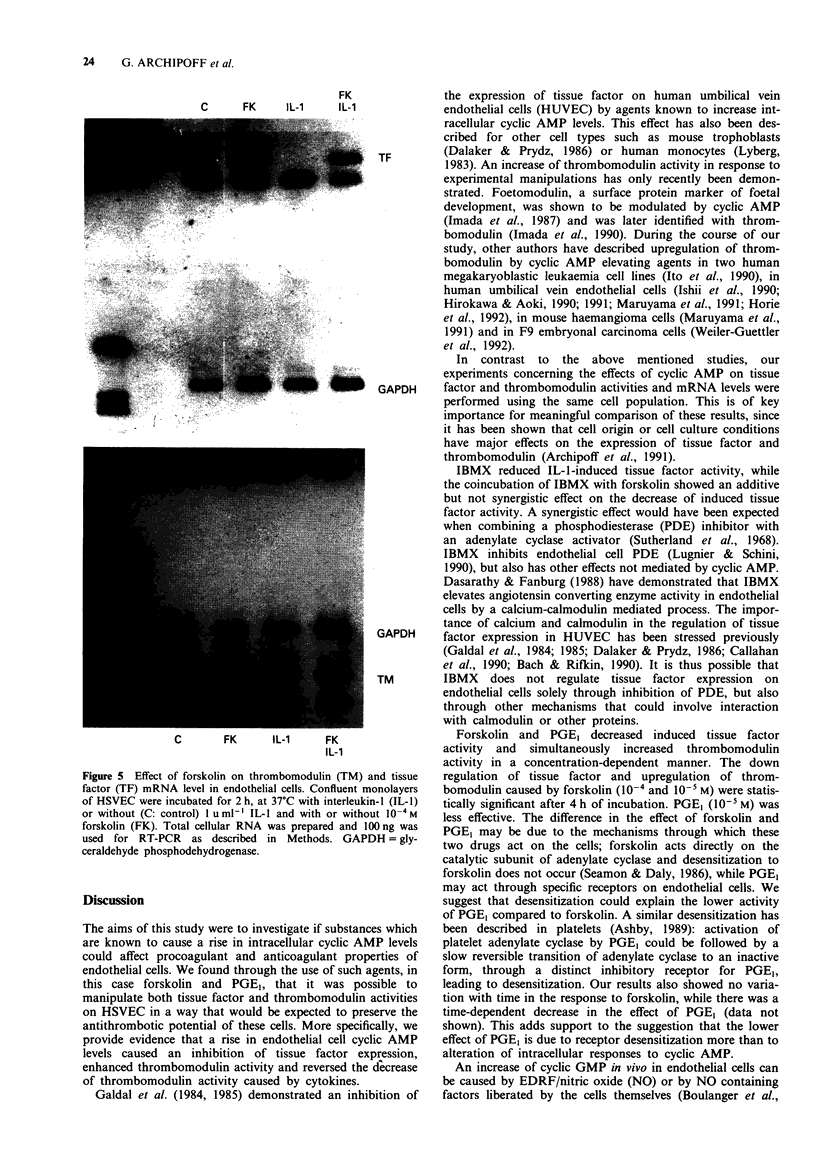
1. The effects of forskolin, prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), dibutyryl cyclic AMP (db cyclic AMP), dibutyryl cyclic GMP (db cyclic GMP) and 3-isobutyl-l-methyl-xanthine (IBMX) were investigated on the expression of tissue factor and thrombomodulin activities on the surface of human saphenous vein endothelial cells (HSVEC) in culture. 2. Forskolin (10(-6) to 10(-4) M), PGE1 (10(-7) to 10(-5) M) and db cyclic AMP (10(-4) to 10(-3) M) caused a concentration-dependent decrease of cytokine-induced tissue factor activity. 3. Similar concentrations of forskolin, PGE1 and db cyclic AMP enhanced significantly constitutive thrombomodulin activity and reversed the decrease of this activity caused by interleukin-1 (IL-1). 4. IBMX (10(-4) M) decreased tissue factor activity and enhanced the effect of forskolin on tissue factor and thrombomodulin activities. 5. Forskolin (10(-4) M) decreased the IL-1-induced tissue factor mRNA and increased the thrombomodulin mRNA level. IL-1 did not change the thrombomodulin mRNA level after 2 h of incubation with HSVEC in culture. 6. Dibutyryl cyclic GMP (10(-4) M to 10(-3) M) did not influence tissue factor or thrombomodulin activity. 7. Our data suggest that elevation of intracellular cyclic AMP levels may participate in the regulation of tissue factor and thrombomodulin expression, thus contributing to promote or restore antithrombotic properties of the endothelium.
Full text
PDF


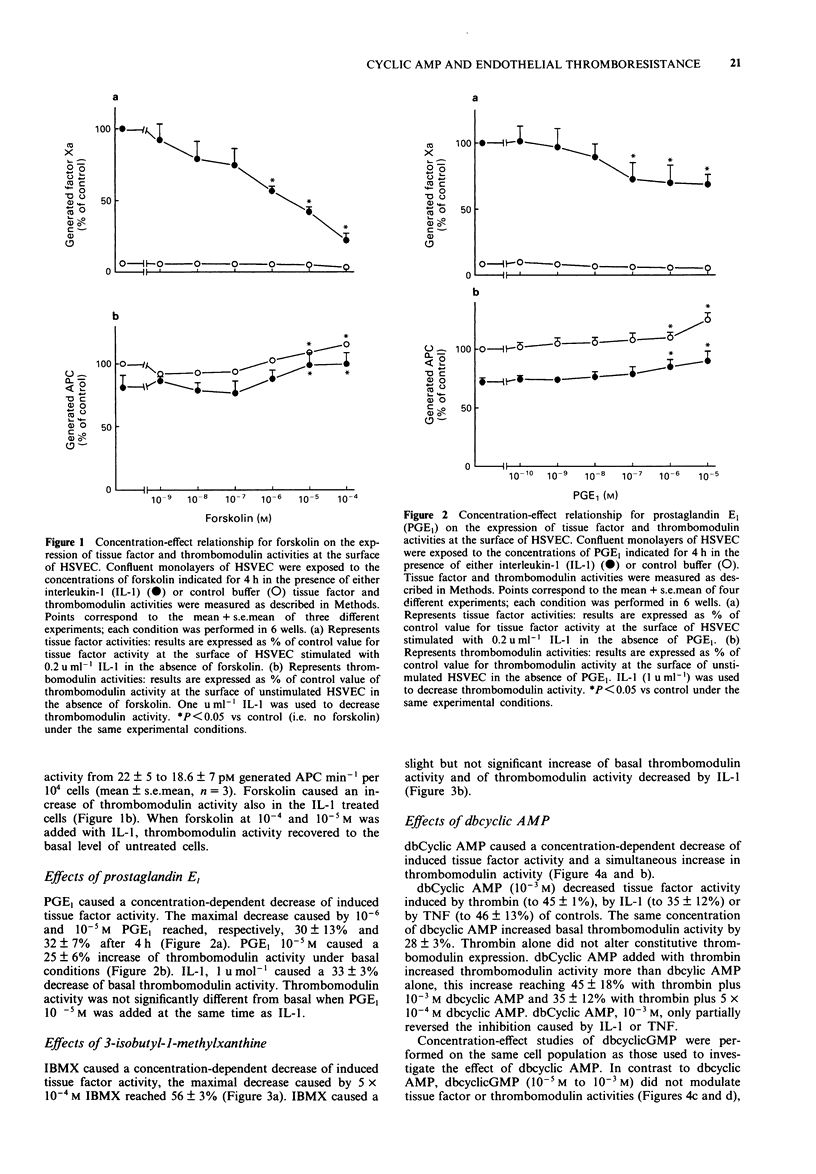




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almus F. E., Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Functional properties of factor VIIa/tissue factor formed with purified tissue factor and with tissue factor expressed on cultured endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Dec 29;62(4):1067–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
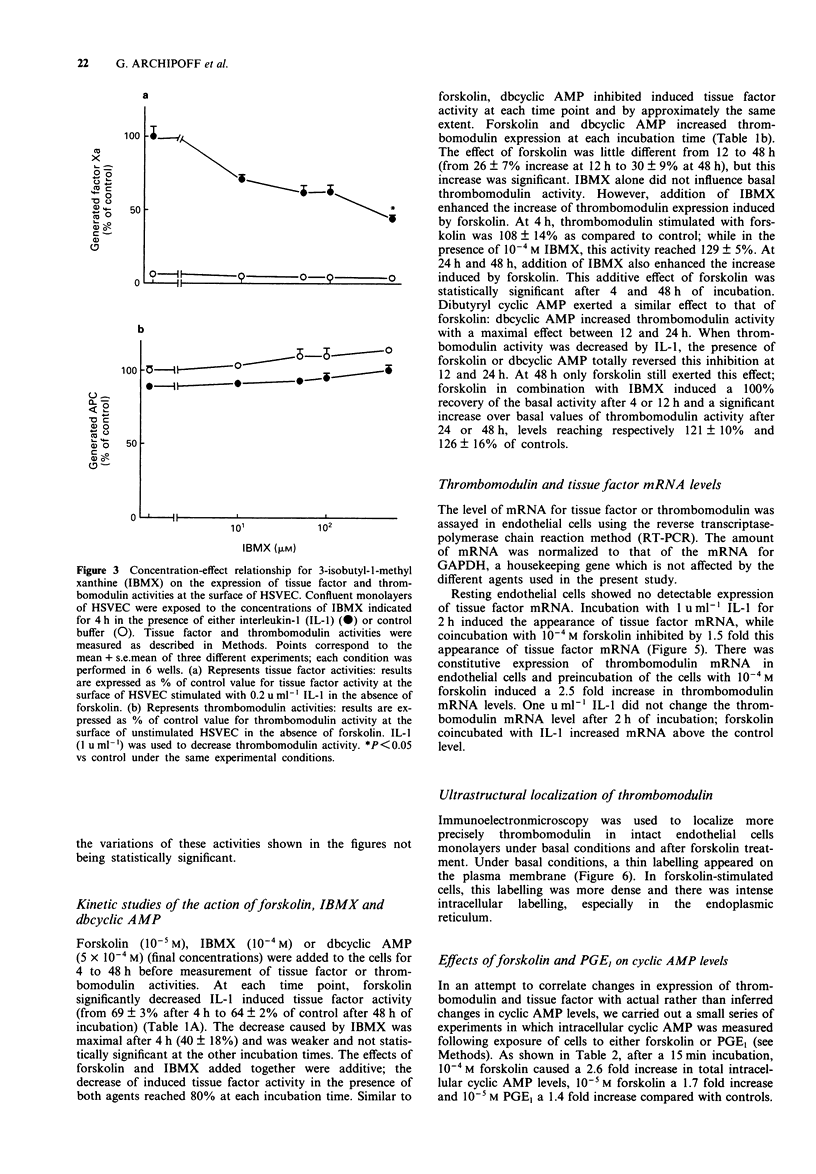
- Archipoff G., Beretz A., Freyssinet J. M., Klein-Soyer C., Brisson C., Cazenave J. P. Heterogeneous regulation of constitutive thrombomodulin or inducible tissue-factor activities on the surface of human saphenous-vein endothelial cells in culture following stimulation by interleukin-1, tumour necrosis factor, thrombin or phorbol ester. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):679–684. doi: 10.1042/bj2730679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby B. Model of prostaglandin-regulated cyclic AMP metabolism in intact platelets: examination of time-dependent effects on adenylate cyclase and phosphodiesterase activities. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;36(6):866–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashida S., Sakuma K. Demonstration of functional compartments of cyclic AMP in rat platelets by the use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;25:229–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R., Rifkin D. B. Expression of tissue factor procoagulant activity: regulation by cytosolic calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6995–6999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beretz A., Freyssinet J. M., Gauchy J., Schmitt D. A., Klein-Soyer C., Edgell C. J., Cazenave J. P. Stability of the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex on the surface of endothelial cells from human saphenous vein or from the cell line EA.hy 926. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2590035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeri D., Almus F. E., Maiello M., Cagliero E., Rao L. V., Lorenzi M. Modification of tissue-factor mRNA and protein response to thrombin and interleukin 1 by high glucose in cultured human endothelial cells. Diabetes. 1989 Feb;38(2):212–218. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger C., Schini V. B., Moncada S., Vanhoutte P. M. Stimulation of cyclic GMP production in cultured endothelial cells of the pig by bradykinin, adenosine diphosphate, calcium ionophore A23187 and nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):152–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan K. S., Blumenthal D. K., Fair D. S. Tissue factor expression in human endothelial cells is regulated by calcium/calmodulin. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1990;24:449–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnocha S. A., Eskin S. G., Hall E. R., McIntire L. V. Permeability of human endothelial monolayers: effect of vasoactive agonists and cAMP. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Nov;67(5):1997–2005. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.5.1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway E. M., Bach R., Rosenberg R. D., Konigsberg W. H. Tumor necrosis factor enhances expression of tissue factor mRNA in endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 1989 Feb 1;53(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossman D. C., Carr D. P., Tuddenham E. G., Pearson J. D., McVey J. H. The regulation of tissue factor mRNA in human endothelial cells in response to endotoxin or phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9782–9787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalaker K., Prydz H. Effect of some drugs on thromboplastin activity in mouse trophoblast cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 15;35(20):3433–3439. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90609-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasarathy Y., Fanburg B. L. Elevation of angiotensin converting enzyme by 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine in cultured endothelial cells: a possible role for calmodulin. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Oct;137(1):179–184. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman W. A., Majerus P. W. Structure and function of thrombomodulin: a natural anticoagulant. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4743–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo L. F. The complexity of endothelial cells. A review. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Aug;92(2):241–250. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/92.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet J. M., Beretz A., Klein-Soyer C., Gauchy J., Schuhler S., Cazenave J. P. Interference of blood-coagulation vitamin K-dependent proteins in the activation of human protein C. Involvement of the 4-carboxyglutamic acid domain in two distinct interactions with the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex and with phospholipids. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):501–507. doi: 10.1042/bj2560501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdal K. S., Lyberg T., Evensen S. A., Nilsen E., Prydz H. Inhibition of the thromboplastin response of endothelial cells in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 1;33(17):2723–2726. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90687-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdal K. S., Lyberg T., Evensen S. A., Nilsen E., Prydz H. Thrombin induces thromboplastin synthesis in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Aug 30;54(2):373–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach H., Lieberman H., Bach R., Godman G., Brett J., Stern D. Enhanced responsiveness of endothelium in the growing/motile state to tumor necrosis factor/cachectin. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):913–931. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerzer R., Karrenbrock B., Siess W., Heim J. M. Direct comparison of the effects of nitroprusside, SIN 1, and various nitrates on platelet aggregation and soluble guanylate cyclase activity. Thromb Res. 1988 Oct 1;52(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas T. A., Bertomeu M. C., Bastida E., Buchanan M. R. Cyclic AMP regulation of endothelial cell triacylglycerol turnover, 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-HODE) synthesis and endothelial cell thrombogenicity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 19;1051(2):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90190-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa K., Aoki N. Regulatory mechanisms for thrombomodulin expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Apr;147(1):157–165. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041470120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa K., Aoki N. Up-regulation of thrombomodulin in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. J Biochem. 1990 Nov;108(5):839–845. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie S., Kizaki K., Ishii H., Kazama M. Retinoic acid stimulates expression of thrombomodulin, a cell surface anticoagulant glycoprotein, on human endothelial cells. Differences between up-regulation of thrombomodulin by retinoic acid and cyclic AMP. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):149–154. doi: 10.1042/bj2810149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada M., Imada S., Iwasaki H., Kume A., Yamaguchi H., Moore E. E. Fetomodulin: marker surface protein of fetal development which is modulatable by cyclic AMP. Dev Biol. 1987 Aug;122(2):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada S., Yamaguchi H., Nagumo M., Katayanagi S., Iwasaki H., Imada M. Identification of fetomodulin, a surface marker protein of fetal development, as thrombomodulin by gene cloning and functional assays. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90058-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H., Kizaki K., Uchiyama H., Horie S., Kazama M. Cyclic AMP increases thrombomodulin expression on membrane surface of cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 1990 Sep 1;59(5):841–850. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90397-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Ogura M., Morishita Y., Takamatsu J., Maruyama I., Yamamoto S., Ogawa K., Saito H. Enhanced expression of thrombomodulin by intracellular cyclic AMP-increasing agents in two human megakaryoblastic leukemia cell lines. Thromb Res. 1990 Jun 15;58(6):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khym J. X. An analytical system for rapid separation of tissue nucleotides at low pressures on conventional anion exchangers. Clin Chem. 1975 Aug;21(9):1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi Y., Ashikaga T., Numano F. Phosphodiesterases in vascular endothelial cells. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;25:201–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Soyer C., Beretz A., Millon-Collard R., Abecassis J., Cazenave J. P. A simple in vitro model of mechanical injury of confluent cultured endothelial cells to study quantitatively the repair process. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Oct 21;56(2):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langeler E. G., van Hinsbergh V. W. Norepinephrine and iloprost improve barrier function of human endothelial cell monolayers: role of cAMP. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):C1052–C1059. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.5.C1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugnier C., Schini V. B. Characterization of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 1;39(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90650-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyberg T. Effect of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP on thromboplastin (factor III) synthesis in human monocytes in vitro. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Dec 30;50(4):804–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier J. A., Hla T., Maciag T. Cyclooxygenase is an immediate-early gene induced by interleukin-1 in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10805–10808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I., Majerus P. W. The turnover of thrombin-thrombomodulin complex in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and A549 lung cancer cells. Endocytosis and degradation of thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15432–15438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I., Soejima Y., Osame M., Ito T., Ogawa K., Yamamoto S., Dittman W. A., Saito H. Increased expression of thrombomodulin on the cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and mouse hemangioma cells by cyclic AMP. Thromb Res. 1991 Feb 1;61(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marín J., Sánchez-Ferrer C. F. Role of endothelium-formed nitric oxide on vascular responses. Gen Pharmacol. 1990;21(5):575–587. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(90)91002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. L., Andreoli S. P., Esmon N. L., Esmon C. T., Bang N. U. Endotoxin enhances tissue factor and suppresses thrombomodulin expression of human vascular endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):124–130. doi: 10.1172/JCI112772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. L., Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L. Tumor necrosis factor leads to the internalization and degradation of thrombomodulin from the surface of bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Handley D. A., Esmon C. T., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell procoagulant while suppressing cell-surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Blaine E. H., Greenwald J. E., Michener M. L., Saper C. B., Stockmann P. T., Tolunay H. E. The biochemical pharmacology of atrial peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:23–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Tissue factor and hemostasis. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C. D., Challiss R. A., Shahid M. Differential modulation of tissue function and therapeutic potential of selective inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jan;12(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90484-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi M., Sakai T., Kisiel W. Correlation between antigenic and functional expression of tissue factor on the surface of cultured human endothelial cells following stimulation by lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. Thromb Res. 1989 Jul 1;55(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90459-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen K. S., Wiiger M. T., Narahara N., Andoh K., Gaudernack G., Prydz H. Induction of tissue factor synthesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells involves protein kinase C. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Apr 2;67(4):473–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vuento M., Engvall E. Interaction of fibronectin with antibodies and collagen in radioimmunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 21;534(2):210–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santell L., Levin E. G. Cyclic AMP potentiates phorbol ester stimulation of tissue plasminogen activator release and inhibits secretion of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 from human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16802–16808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpati E. M., Sadler J. E. Regulation of endothelial cell coagulant properties. Modulation of tissue factor, plasminogen activator inhibitors, and thrombomodulin by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20705–20713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpati E. M., Wen D., Broze G. J., Jr, Miletich J. P., Flandermeyer R. R., Siegel N. R., Sadler J. E. Human tissue factor: cDNA sequence and chromosome localization of the gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5234–5238. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Diocee B. K., Martin W., Moodie S. A. Pig aortic endothelial-cell cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors to evaluate their roles in regulating cyclic nucleotide levels in intact cells. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):127–132. doi: 10.1042/bj2660127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tougard C., Picart R. Use of pre-embedding ultrastructural immunocytochemistry in the localization of a secretory product and membrane proteins in cultured prolactin cells. Am J Anat. 1986 Feb-Mar;175(2-3):161–177. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001750206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien W. H., Sass S. P., Sheppard H. The lack of correlation between inhibition of aggregation and cAMP levels with canine platelets. Thromb Res. 1982 Nov 15;28(4):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler-Guettler H., Yu K., Soff G., Gudas L. J., Rosenberg R. D. Thrombomodulin gene regulation by cAMP and retinoic acid in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2155–2159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D. Z., Dittman W. A., Ye R. D., Deaven L. L., Majerus P. W., Sadler J. E. Human thrombomodulin: complete cDNA sequence and chromosome localization of the gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4350–4357. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Furumichi T., Furui H., Yokoi T., Ito T., Yamauchi K., Yokota M., Hayashi H., Saito H. Roles of calcium, cyclic nucleotides, and protein kinase C in regulation of endothelial permeability. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):410–420. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Suprenant Y. M. Induction of endothelial cell/macrophage procoagulant activity: synergistic stimulation by gamma interferon and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Apr 25;61(2):178–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]