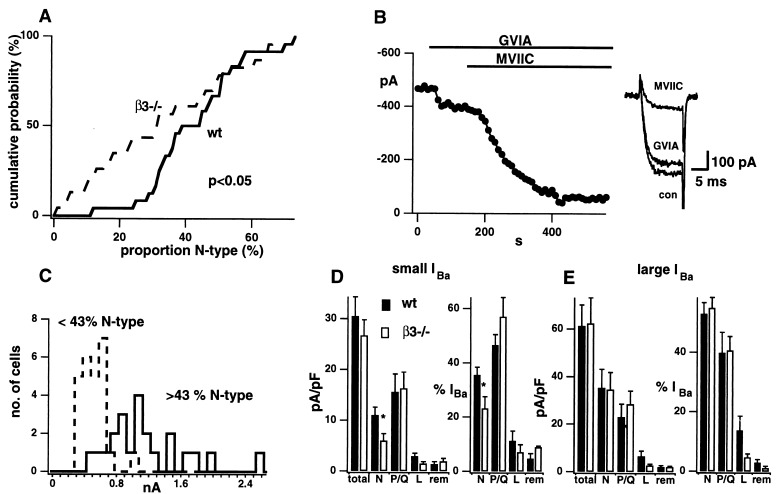
Figure 3.
The N-type current is reduced in β3−/− SCG neurons. (A) The cumulative probability plot for the proportion of IBa that is N-type for 24 wt (solid) and 23 β3−/− (broken) SCG neurons. Plots were significantly different by Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (P < 0.05). (B) Histogram of IBa magnitude in which neurons have been divided according to whether the percentage of IBa carried by N-type channels was <43 (dashed histogram) or >43 (solid histogram). The difference in average IBa between these groups was clearly significant, regardless of whether wt and β3−/− cells were lumped together as shown, or treated separately. Average values of IBa were 440 ± 55 vs. 1061 ± 153 pA for wt neurons (P < 0.01) and 425 ± 38 vs. 1013 ± 146 pA for β3−/− cells (P < 0.001). (C) Effect of 1 μM GVIA and 10 μM MVIIC on IBa in β3−/− neuron with IBa < 700 pA. Exemplar traces on the right. Histograms of the current density and proportion of small (D; n = 6–16) or large (E; n = 3–11) IBa carried by total, N, P/Q, L ,or remainder channels types for wt (solid) and β3−/− (open). N-type current density and proportion are significantly reduced in small IBa β3−/− neurons (∗ indicates P < 0.05 by Student’s t test).