Abstract
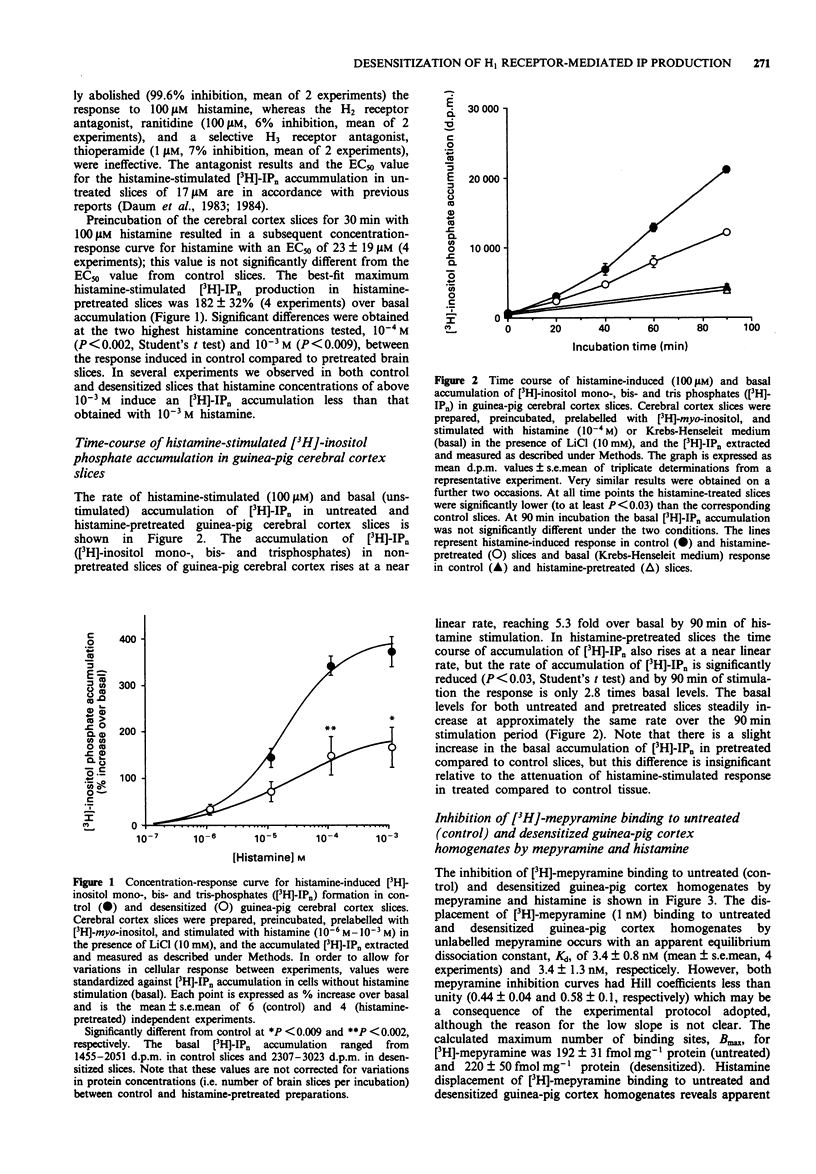
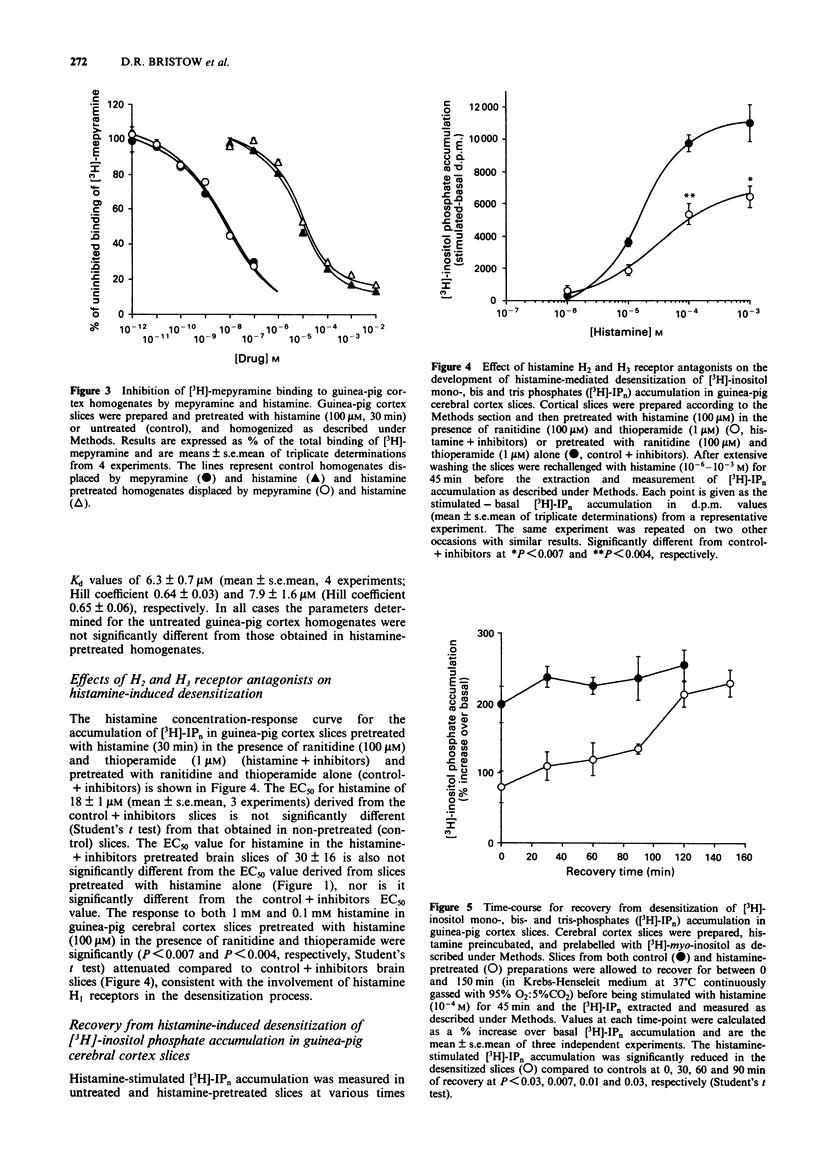
1. Histamine stimulated the production of [3H]-inositol phosphates in untreated (control) guinea-pig cerebral cortex slices with a best-fit EC50 of 17 +/- 4 microM, and a best-fit maximum response of 385 +/- 23% over basal accumulation. 2. Histamine pretreatment desensitized guinea-pig cortex slices to a subsequent challenge with histamine, which was observed as a reduction in the best-fit maximum response to 182 +/- 32% over basal accumulation. 3. The time-course for the histamine-induced production of [3H]-inositol phosphates was approximately linear over 90 min of stimulation in both control and histamine pretreated slices. The rate of production in pretreated slices was significantly slowed compared to control, such that by 90 min of histamine stimulation the desensitized slices produced 2.8 times the basal [3H]-inositol phosphate accumulation compared to 5.3 fold the basal [3H]-inositol phosphate accumulation in the control slices. 4. Displacement of [3H]-mepyramine binding to homogenates of guinea-pig cerebral cortex by mepyramine and histamine revealed that histamine pretreatment did not alter the apparent affinity of the H1 receptor for histamine (control Kd = 6.3 +/- 0.7 microM, desensitized Kd = 7.9 +/- 1.6 microM) or mepyramine (control Kd = 3.4 +/- 0.8 nM, desensitized Kd = 3.4 +/- 1.3 nM), nor was there any reduction in the calculated maximum number of [3H]-mepyramine binding sites (control Bmax = 192 +/- 31 fmol mg-1 protein, desensitized Bmax = 220 +/- 50 fmol mg-1 protein).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bristow D. R., Young J. M. Characteristics of histamine-induced inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in HeLa cells. Agents Actions Suppl. 1991;33:387–392. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7309-3_28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodde O. E., Michel M. C. Disease states can modify both receptor number and signal transduction pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):383–384. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. D., Prendiville P., Cain C. Alpha 1-adrenergic and H1-histamine receptor control of intracellular Ca2+ in a muscle cell line: the influence of prior agonist exposure on receptor responsiveness. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;29(6):531–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Synder S. H. Histamine H1-receptor binding sites in guinea pig brain membranes: regulation of agonist interactions by guanine nucleotides and cations. J Neurochem. 1980 Apr;34(4):916–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowlen M. S., Barnes M. R., Toews M. L. Regulation of histamine H1 receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis by histamine and phorbol esters in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar 13;188(2-3):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90045-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford M. L., Carswell H., Young J. M. gamma-Aminobutyric acid inhibition of histamine-induced inositol phosphate formation in guinea-pig cerebellum: comparison with guinea-pig and rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):867–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum P. R., Downes C. P., Young J. M. Histamine stimulation of inositol 1-phosphate accumulation in lithium-treated slices from regions of guinea pig brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Jul;43(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum P. R., Downes C. P., Young J. M. Histamine-induced inositol phospholipid breakdown mirrors H1-receptor density in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar 4;87(4):497–498. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon-Carter O., Chuang D. M. Homologous desensitization of muscarinic cholinergic, histaminergic, adrenergic, and serotonergic receptors coupled to phospholipase C in cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):598–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J., Hill S. J. Selective enhancement of histamine H1-receptor responses in guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle by 1,4-dithiothreitol. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):191–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Earp H. S., Harden T. K. Long-term phorbol ester treatment down-regulates protein kinase C and sensitizes the phosphoinositide signaling pathway to hormone and growth factor stimulation. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C in agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7610–7619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J. Distribution, properties, and functional characteristics of three classes of histamine receptor. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Mar;42(1):45–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Greengard P. Regulation of neurotransmitter receptor desensitization by protein phosphorylation. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90211-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leurs R., Smit M. J., Bast A., Timmerman H. Different profiles of desensitization dynamics in guinea-pig jejunal longitudinal smooth muscle after stimulation with histamine and methacholine. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;101(4):881–888. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14175.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Santell L. Thrombin- and histamine-induced signal transduction in human endothelial cells. Stimulation and agonist-dependent desensitization of protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):174–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lurie K. G., Tsujimoto G., Hoffman B. B. Desensitization of alpha-1 adrenergic receptor-mediated vascular smooth muscle contraction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jul;234(1):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. W., Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of a P2Y-purinergic receptor-regulated phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19535–19539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough P. M., Eubanks J. H., Brown J. H. Desensitization and recovery of muscarinic and histaminergic Ca2+ mobilization in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):135–141. doi: 10.1042/bj2490135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi M., Payan D. G. Phorbol ester-mediated desensitization of histamine H1 receptors on a cultured smooth muscle cell line. Life Sci. 1988;43(18):1433–1440. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. K., Bennett C. F., Fluharty S. J., Kotlikoff M. I. Mechanism of phorbol ester inhibition of histamine-induced IP3 formation in cultured airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):L209–L216. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.4.L209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata N., Harden T. K. Regulation of inositol trisphosphate accumulation by muscarinic cholinergic and H1-histamine receptors on human astrocytoma cells. Differential induction of desensitization by agonists. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):337–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2410337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quach T. T., Duchemin A. M., Rose C., Schwartz J. C. Specific desensitization of histamine H1 receptor-mediated [3H]glycogen hydrolysis in brain slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;20(2):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. R., Albers F. J., Middleton J. P., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Obeid L. M., Dennis V. W. 5-HT1A and histamine H1 receptors in HeLa cells stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and phosphate uptake via distinct G protein pools. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):372–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickels K., Case W. G., Downing R. W., Winokur A. Long-term diazepam therapy and clinical outcome. JAMA. 1983 Aug 12;250(6):767–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharps E. S., McCarl R. L. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method to measure 32P incorporation into phosphorylated metabolites in cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M. J., Bloemers S. M., Leurs R., Tertoolen L. G., Bast A., de Laat S. W., Timmerman H. Short-term desensitization of the histamine H1 receptor in human HeLa cells: involvement of protein kinase C dependent and independent pathways. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):448–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. E., Richelson E. Desensitization of histamine H1 receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 May;15(3):462–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treherne J. M., Young J. M. [3H]-(+)-N-methyl-4-methyldiphenhydramine, a quaternary radioligand for the histamine H1-receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):797–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H., Inagaki N., Yamatodani A., Watanabe T. Is the histaminergic neuron system a regulatory center for whole-brain activity? Trends Neurosci. 1991 Sep;14(9):415–418. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90034-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


