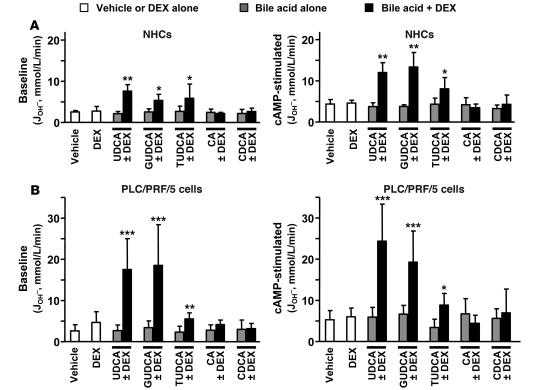
Figure 3. The combination of UDCA and dexamethasone increases AE activities in hepatobiliary cells.
Cl–/HCO3– AE activity was determined by microfluorimetry in NHCs (A) and PLC/PRF/5 cells (B) following treatments for 24 hours with either dexamethasone and/or UDCA, GUDCA, TUDCA, CA, or CDCA (100 μM each) or with just vehicle. Treated cells were analyzed for AE activities, both baseline (left) and in the presence of a cAMP-stimulation mixture (right). The AE activity was estimated as the rate of pHi recovery from propionate-induced intracellular alkalinization. Rates of pHi change were measured as δpHi/δt from the tangent to the experimental plot; transmembrane acid fluxes (or equivalent transmembrane base fluxes, JOH– [mmol/l/min]) were calculated as βtot × δpHi/δt, where βtot is the total intracellular buffering power in the presence of CO2/HCO3–. Data are mean ± SD; n = 9 each. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus vehicle control.