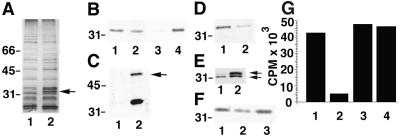
Figure 5.
Biochemical characterization of proteins bound to chemical compound matrices and effects of the compound on DNA replication. (A) Silver-stained gel of proteins eluted from C-matrix (lane 1) and P-matrix (lane 2). The arrow marks a band at 34 kDa specific for P-matrix. (B) Western blot analysis of 1 μl of total extract treated with C-matrix (lane 1) or P-matrix (lane 2). Proteins eluted from C-matrix (lane 3) and P-matrix (lane 4) are equivalent to proteins retrieved from 10 μl of extract. The blot is probed with anti-CDK1 antibodies and shows that CDK1 is found on P-matrix but not C-matrix, resulting in a partial depletion of CDK1 from P-matrix-treated extracts. (C) Western blot of C-matrix (lane 1) and P-matrix (lane 2) probed with both anti-CDK1 and anti-Xenopus cyclin B antibodies. The arrow indicates cyclin B, which is present only on P-matrix. (D) Western blot of proteins eluted from P-matrix incubated in extracts in the presence of DMSO (lane 1) or 100 μM AP (lane 2) and probed with anti-CDK1 antibodies. Less CDK1 binds to the matrix in the presence of the free compound. (E) Western blot of proteins eluted from C-matrix (lane 1) and P-matrix (lane 2) probed with both anti-CDK1 and anti-CDK2 antibodies. A small amount of CDK2 binds to both matrices, whereas CDK1 binding is specific for P-matrix. Upper arrow, CDK1 at 34 kDa; lower arrow, CDK2 at 32 kDa. (F) Western blot probed with anti-CDK1 antibodies showing the amount of CDK1 remaining in C-matrix-treated extracts (lane 1), P-matrix-treated extracts (lane 2), and P-matrix-treated extracts that have been rescued by the addition of pure CDK1–cyclin B (lane 3). Addition of pure kinase restores CDK1 to normal levels. (G) DNA replication experiment showing that similar amounts of [32P]dCTP are incorporated into immobilized plasmid DNA in interphase extracts in control reactions (1) and reactions containing 200 μM (3) or 300 μM (4) AP. Incorporation is inhibited by aphidicolin at 50 μg/ml, a specific inhibitor of DNA replication (2).