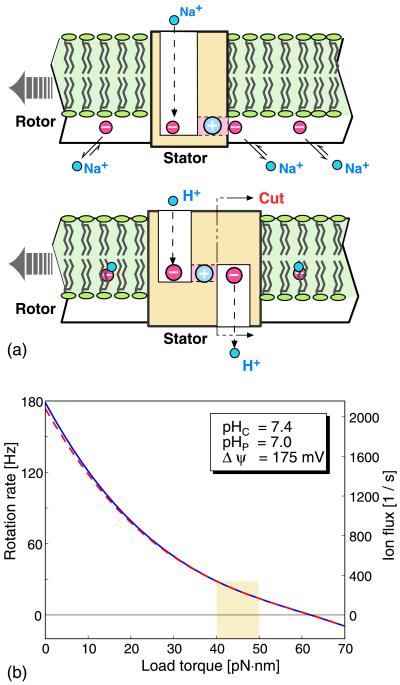
Figure 8.
(a) The relationship between the one-channel model of P. modestum (Upper) and the two-channel model of E. coli (Lower) (33). In E. coli the rotor sites (D61) may not be accessible from the cytoplasm, but only via a cytoplasmic half-channel. In the sodium motor the cytoplasmic channel is unnecessary because the rotor sites (E65) are accessible directly to the cytoplasmic reservoir. The E. coli stator can be converted to the P. modestum stator simply by cutting off the cytoplasmic channel and moving the row of rotor sites below the membrane level. (b) Comparison of the load–velocity curves for the one-channel model (solid line) and the two-channel model (broken line) applied to the proton-driven E. coli motor. The two models perform practically the same.