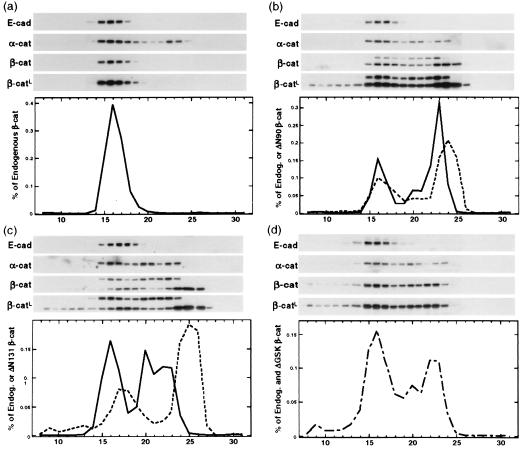
Figure 2.
Accumulation of low-molecular-mass β-catenin pools in MDCK clones expressing mutant β-catenin. Proteins extracted from MDCK clones ΔN90-A/+Dox (a) ΔN90-A/-Dox (b), ΔN131-D/-Dox (c), and ΔGSK-4/-Dox (d) were fractionated by Superose 6 size-exclusion chromatography as described in Materials and Methods. Equal amounts of fractions 8–31 were separated by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies specific for E-cadherin, α-catenin, and β-catenin; a second, longer exposure of the β-catenin immunoblots (β-catL) is shown to visualize small amounts of mutant β-catenin in high-molecular-mass fractions 8–10. The β-catenin antibody detected both endogenous β-catenin (single band in a and higher-molecular-mass bands in b and c) and ΔN90 or ΔN131 β-catenins (lower-molecular-mass bands in b and c). The single β-catenin band in d represents the total of both endogenous and ΔGSK β-catenin because the electrophoretic mobility of endogenous and ΔGSK β-catenin was very similar (see Fig. 1). β-Catenin immunoblots were quantified, and protein concentrations in each fraction were measured as percentage of all endogenous (solid lines in a–c), percentage of all mutant (dotted lines in b and c), and percentage of total (sum of endogenous and ΔGSK β-catenin; dashed line in d).