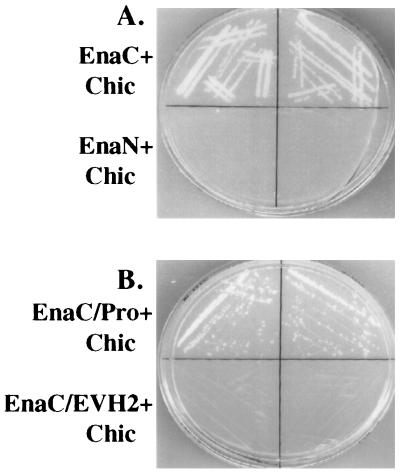
Figure 1.
Identification of chickadee as a binding partner for Ena in a yeast two-hybrid screen. (A) The first 235 amino acids of Ena (EnaN) and last 243 amino acids of Ena (EnaC) were fused to the sequence encoding the GAL4 DNA binding domain in the pAS1-CYH2 vector. These two constructs were cotransformed with GAL4AD-chickadee (Chic), a clone in which the full-length chickadee coding sequences were fused to the sequence encoding the GAL4 activation domain and which was isolated in a yeast two-hybrid screen by using the C-terminal 243 amino acids of Ena as bait. From each of the cotransformations, two independent clones were spread on medium lacking histidine and analyzed for growth. EnaC, which contains two putative profilin binding sites, can interact with chickadee, whereas EnaN, which contains no putative binding sites for profilin, cannot. (B). Amino acids 440–490 from EnaC containing the putative profilin binding sites (EnaC/Pro) and amino acids 490–684 from EnaC lacking any putative profilin binding sites (EnaC/EVH2) were fused to the DNA binding domain of the yeast transcription factor GAL4 and cotransformed with GAL4AD chickadee. Cotransformed yeast was spread on medium lacking histidine and analyzed for growth. EnaC/Pro can interact with chickadee, whereas EnaC/EVH2 cannot.