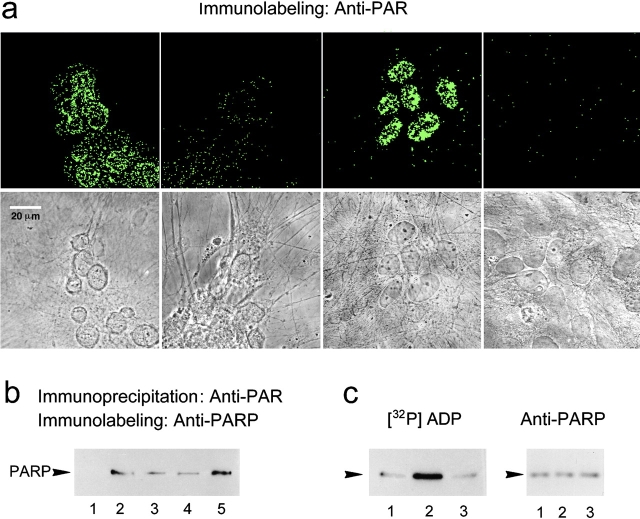
Figure 1.
Membrane depolarization induces polyADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins in brain cortical neurons. (a) PolyADP-ribosylated proteins in the nuclei of prefixed cultured rat cortical neurons were immunolabeled in situ with monoclonal antibody directed against ADP-ribose polymers (10H; see Materials and Methods). Confocal images of neurons, labeled with fluorescein-conjugated secondary antibody (top), were also visualized in transmitted light (bottom). The four frames, from left to right, show neurons depolarized by high-[K+] for 5 min; unstimulated neurons; neurons pretreated with H2O2 (1 mM, 10 min); and depolarized neurons labeled only with the secondary antibody (n = 4). (b) Western blots of polyADP-ribosylated PARP immunoprecipitated by 10H antibody from nuclei of unstimulated (lane 1) and depolarized (lanes 2–4) cortical neurons. Neurons were depolarized by high-[K+] (lane 2), or stimulated by a 2-min train of repetitive (100 Hz) 30-volt, 0.1 ms pulses (lane 3), or by a 10-min train of repetitive (10 Hz) 30-volt, 0.1 ms pulses (lane 4). (Lane 5) Neurons pretreated with H2O2. Immunoprecipitated PARP was immunolabeled by anti-PARP, Vic-5 antibody (n = 6). (c, left) Autoradiograms presenting [32P]polyADP-ribosylated PARP (5 min, 37°C) in isolated nuclei of unstimulated neurons (lane 2) and depolarized neurons (high-[K+]; lane 1, stimulated by a 2-min train of repetitive [100 Hz] 30-volt, 0.1 ms pulses; lane 3). [32P]polyADP-ribosylated PARP was immunoprecipitated from the nuclear protein extracts by N-20 antibody (see Materials and Methods), subjected to SDS-PAGE, autoradiographed, electroblotted (Western blot), and immunolabeled (on right) by anti-PARP, Vic-5 antibody (n = 6).