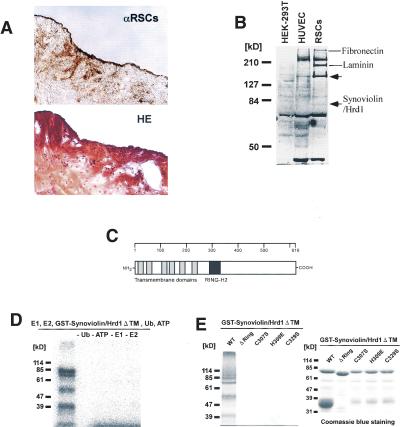
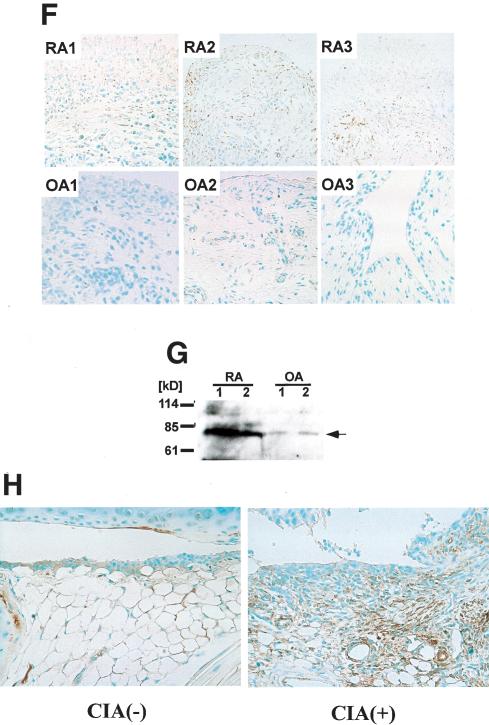
Figure 1.
Molecular cloning and characterization of Synoviolin/Hrd1. (A, top) Immunostaining of synovial tissue derived from RA patient by anti-RSCs antibody. (Bottom) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of synovial tissue derived from the same patient. (B) Western blot analysis using anti-RSCs antibody. Arrows show the RSCs-specific bands. Molecular weights of the specific bands are ∼140 and 83 kD from the top. A 83-kD protein was presumed to be Synoviolin/Hrd1. (HEK-293T) Human embryonic kidney-293T cells; (HUVEC) human umbilical vein endothelial cells. (C) Linear arrangement of Synoviolin/Hrd1. The scale above provides amino acid number. (D) E1- and E2-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of GST-Synoviolin/Hrd1 ΔTM. Reactions were carried out with removed individual components (e.g., E1, E2). (E, left) Synoviolin/Hrd1 RING finger mutants could not mediate auto-ubiquitination. (Right) GST-Synoviolin/Hrd1ΔTM and RING finger mutants were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. There are multiple bands for degradation products of GST-Synoviolin/Hrd1 ΔTM and its mutants. (F) Immunostaining of synovial tissues from RA (top) and OA (bottom) patients by anti-Synoviolin/Hrd1 monoclonal antibody. Representative pictures from RA (n = 5) and OA (n = 5). (G) Western blot analysis using anti-Synoviolin/Hrd1 monoclonal antibody. Lysates prepared from synovial cells derived from RA and OA patients. Arrow indicates endogenous Synoviolin/Hrd1 protein. Representative pictures from RA (n = 5) or OA (n = 5). (H) Immunostaining of synovial tissues in knee joint of control (left) and CIA (right) mouse by anti-Synoviolin/Hrd1 monoclonal antibody. Magnification: A,F, 100×.