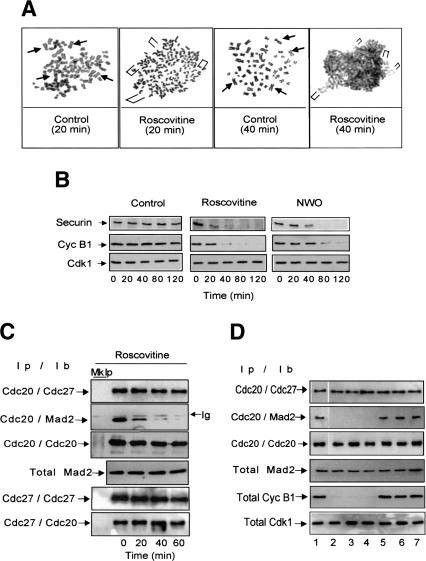
Figure 3.
Cdk inhibition overrides checkpoint-dependent arrest in HeLa cells. Checkpoint-arrested HeLa cells were collected 14 h after nocodazole addition. DMSO, as control, or Roscovitine were then added in the continuous presence of nocodazole and samples taken at the indicated time points. (A) Chromosomes were stained with Giemsa. Arrowheads (Control) or brackets (Roscovitine) indicate maintenance or loss of sister chromatid cohesion. (B) Securin and cyclin B1 were visualized by immunoblot from total cell lysates; securin and cyclin B1 were also visualized from cells taken after nocodazole washout (NWO). In A, sister chromatid cohesion was lost in about 80% of cells 20 min after Roscovitine addition. (C) Cdc20 or Cdc27 were immunoprecipitated from samples taken at the indicated time points from Roscovitine addition (Ip) and associated Cdc27, Cdc20, and Mad2 were detected by immunoblot (Ib); the total amount of Mad2 is also shown. (Mk Ip) Mock precipitations; (Ig) immunoglobulin. (D) Checkpoint-arrested HeLa cells were collected 14 h after nocodazole addition and split into seven dishes. Then, DMSO (lane 1), Alsterpaullone (800 nM; lane 2), Indirubin 3′ monoxime (6 μM; lane 3), Purvalanol A (600 nM; lane 4), UO 126 (30 μM; lane 5), SB 203589 (30 μM; lane 6), and H89 (30 μM; lane 7), were individually added in the continuous presence of nocodazole, and cells harvested after additional 40 min incubation. Cdc20 was immunoprecipitated (Ip) and associated Cdc27 and Mad2 were detected by immunoblot (Ib), the total amount of Mad2, cyclin B1, and cdk1 is also shown. UO 126, SB 203589, and H89 were also tested in a range of concentration from 30 nM to 50 μM giving similar results (not shown).