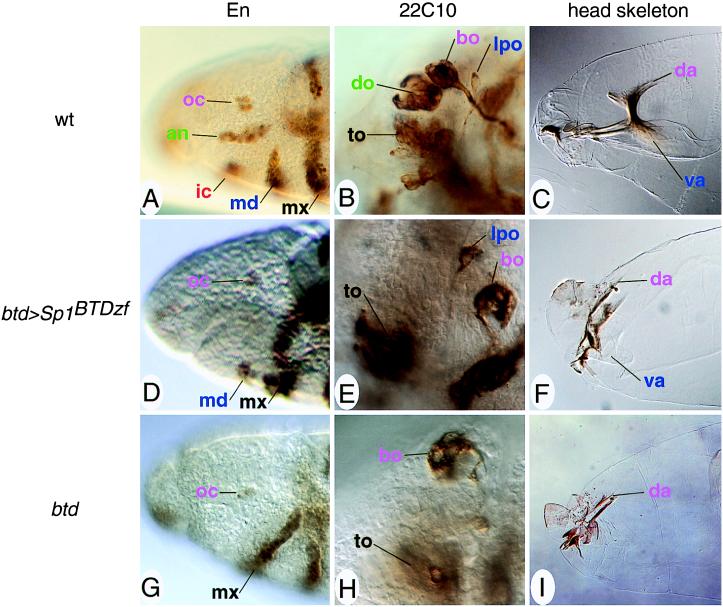
Figure 4.
Head rescue pattern of btd>Sp1BTDzf-bearing btd mutant embryos. (A–C) Head structures of wild-type embryos. (D–F) Head structures of btd>Sp1BTDzf-bearing btd mutant embryos. (G–I) Head structures of btd mutant embryos. (A, D, and G) Anti-En antibody labeling of stage 10 embryos. (Magnification, ×400.) Only the mandibular segment is partially rescued (D); antennal and intercalary segments are missing (compare with A and G). (B, E, and H) mAb22C10 staining of stage 14/15 embryos showing head sensory organs at a representative focal plane. (Magnification, ×1,000.) The lateropharyngeal organ of mandibular origin is rescued whereas the dorsal organ (an antennal organ) is not (E, compare with B and H). (C, F, and I) Head skeletons of stage 17 embryos show that intercalary and antennal cuticle structures are not rescued, whereas the ventral arm of mandibular origin is partially present in Sp1BTDzf-expressing embryos (F). (Magnification, ×400.) Embryos are dorsal up and anterior to the left and staged according to ref. 32. Abbreviations and color code: ocular (oc) segmental structures (bo, Bolwig organ; da, dorsal arms) are labeled in violet; antennal (an) structures (do, dorsal organ) are green; intercalary (ic) structures are orange red; mandibular (md) structures (lpo, lateropharyngeal organ; va, ventral arms) are blue; maxillary (mx) structures (to, terminal organ) are black (for a detailed description of the segmental identity of organs, Engrailed stripes, and cuticle structures, see ref. 28).