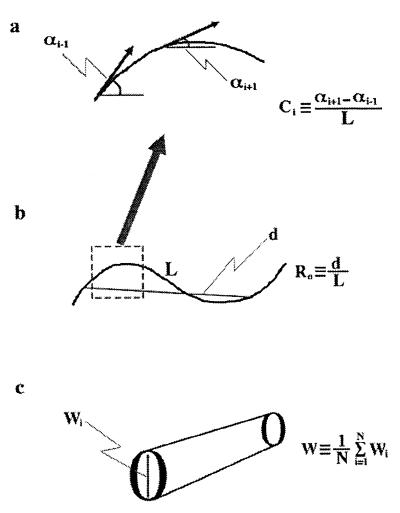
Figure 1.
(a) Curvature of dendrites was defined as the inverse of the curvature radius (Ci). For each dendrite, a mean C value then was determined with the following equation: C = (1/N) Σ⋅Ci, where N is the number of equidistant points along the dendrite. (b) The ratio (Ro) of the end to end distance (d) to the curvilinear length (L) was calculated for each dendrite (Ro = d/L). (c) The width of each dendrite was determined from the average of the sum of all widths along the dendrite (W = (1/N) Σ⋅wi).