Figure 1.
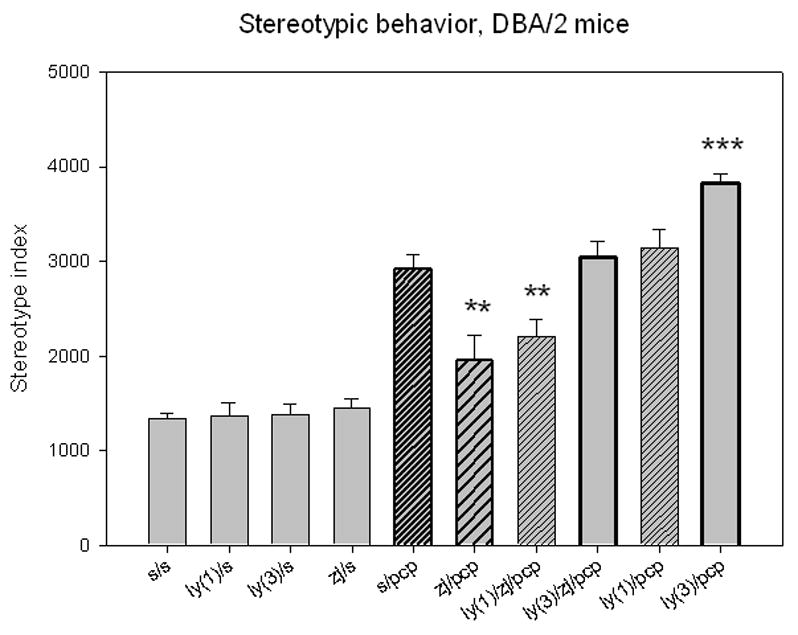
N-Acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) peptidase inhibition reduces phencyclidine (PCP)-induced stereotypic movements in DBA/2 mice. Mice (10 to 15 mice per group) were given two i.p. injections 10 minute apart and their activity monitored in an open field chamber 10 minutes after the last injection. Injection with the group II antagonist LY341495 (1 or 3 mg/kg) or the NAAG peptidase inhibitor, ZJ43 (150mg/kg), followed by saline had the same effect as two injections of saline. Saline followed by 6 mg/kg of PCP induced a significant increase in stereotypic behavior versus each of the other saline groups (p < 0.001). ZJ43 (150 mg/kg) significantly decreased the effects of PCP on stereotypic behavior and this action of ZJ43 was reversed by coinjection of 3mg/kg LY341495 with ZJ43 10 minutes prior to injection of PCP. Preinjection of mice with 3 mg/kg LY341495 alone prior to PCP injection significantly increased the stereotypy above that obtained with saline PCP. (* denotes p<0.05; ** denotes p< 0.01; *** denotes p< 0.001 in this and following figures)
