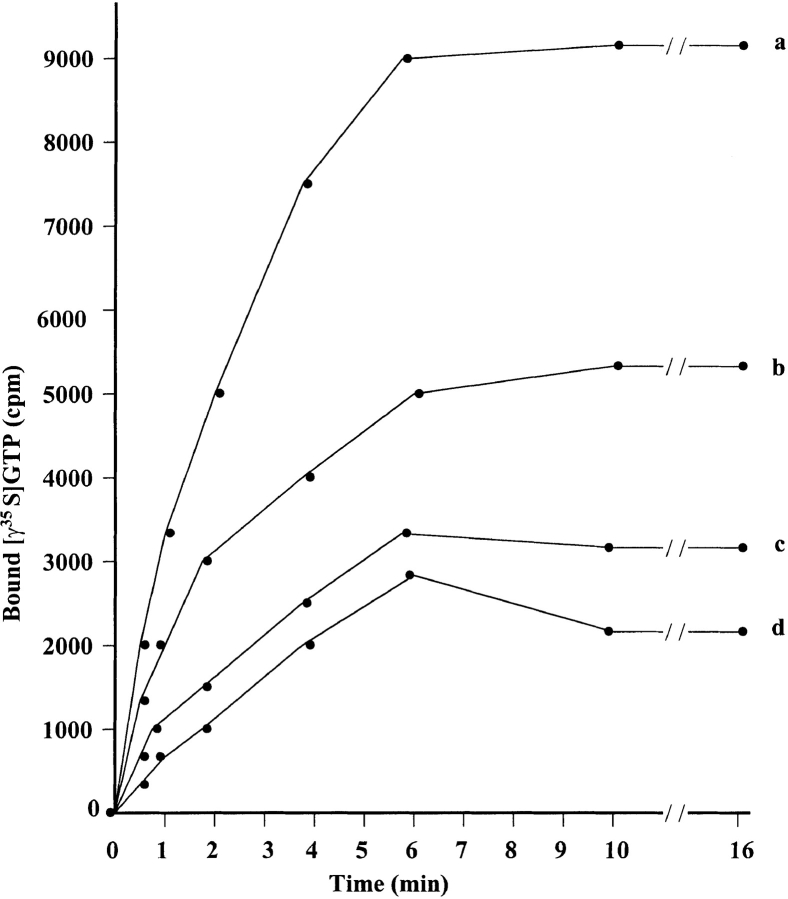
Figure 11.
Kinetics of GTP-γ–35S bound to GDP-loaded GST-Rac1 in the presence of ankyrin-associated Tiam1 isolated from SP-1 cells: transfected with HA-tagged C1199 Tiam1 cDNA (a) or GFP-tagged Tiam1 fragment cDNA (d); or cotransfected with HA-tagged C1199 Tiam1 cDNA plus GFP-tagged Tiam1 fragment cDNA (c) or vector alone (b). Purified E. coli–derived GST-tagged GTPases (e.g., Rac1, Cdc42, or RhoA) were preloaded with GDP. First, 2 pmol ankyrin-associated Tiam1 isolated from various SP1 transfectants was added to the reaction buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 100 μM AMP-PNP, 0.5 mg/ml BSA, and 2.5 μM GTP-γ–35S (∼1,250, Ci/mmol). Subsequently, 2.5 pmol GDP-loaded GST-tagged Rho GTPases (e.g., Rac1, RhoA, Cdc42 or GST alone) were mixed with the reaction buffer containing ankyrin-associated Tiam1 and GTP-γ–35S to initiate the exchange reaction at room temperature. At various time points, the reaction of each sample was terminated by adding ice-cold termination buffer as described in Materials and Methods. The termination reactions were filtered immediately through nitrocellulose filters, and the radioactivity associated with the filters were measured by scintillation fluid. The amount of GTP-γ–35S bound to Tiam1 or control sample (preimmune serum–conjugated Sepharose beads) in the absence of Rho GTPases (e.g., Rac1, Cdc42, or RhoA) was subtracted from the original values. Data represent an average of triplicates from three to five experiments. SD < 5%.