Figure 4.
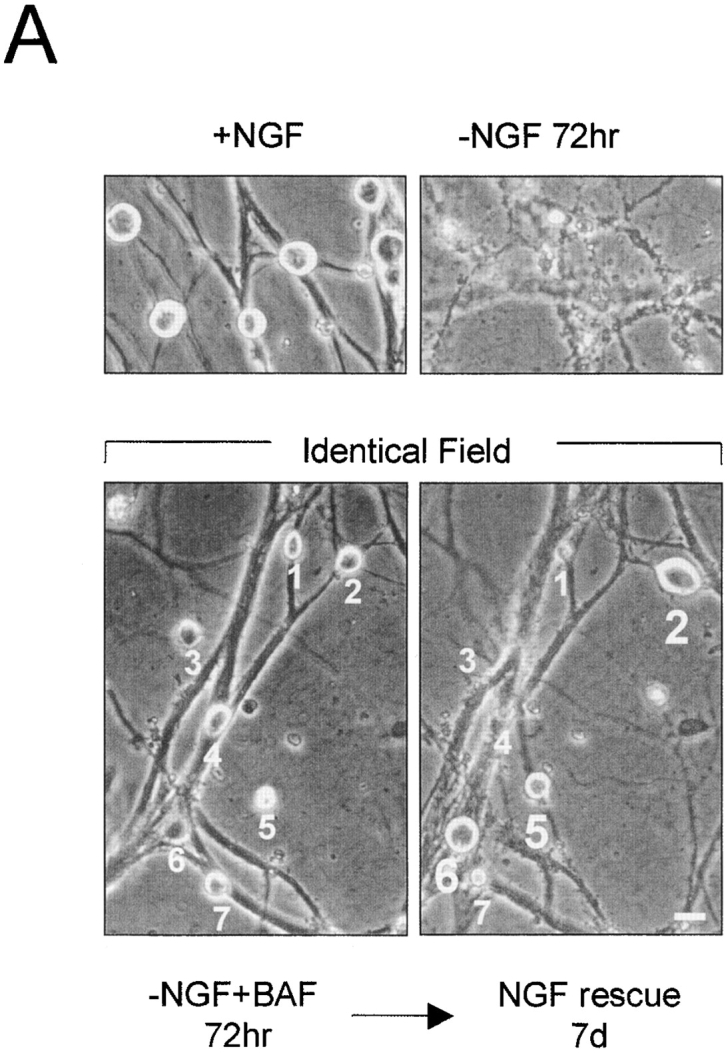
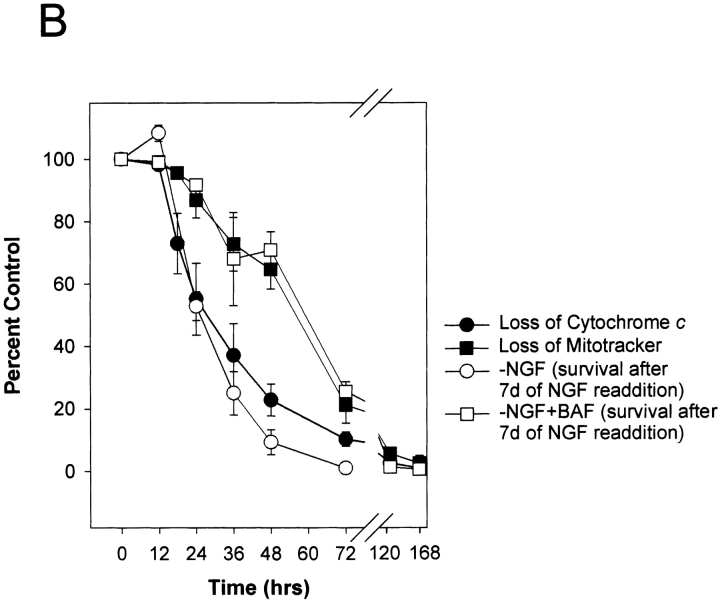
Time course of commitment to death in NGF-deprived sympathetic neurons in the absence or presence of caspase inhibitor. (A) Phase-contrast photographs showing sympathetic neurons rescued with NGF readdition. Representative field of NGF-deprived, BAF-treated cells (72 h of NGF deprivation, 50 μM BAF) showing seven neurons (numbered 1–7) that are prevented from undergoing apoptosis (left; −NGF + BAF 72 h). The same field of cells is shown 7 d after NGF readdition (right; NGF rescue 7d). Cells numbered 2, 5, and 6 were rescued with NGF, whereas cells numbered 1, 3, 4, and 7 were not. Top panels show photographs of control cells that were either maintained in NGF (+NGF) or deprived of NGF without BAF for 72 h (−NGF 72 h). (B) Data showing the percentage of sympathetic neurons capable of recovery with NGF readdition. NGF-maintained mouse sympathetic neurons (5 d in vitro) were deprived of NGF either in the absence (open circles) or presence of 50 μM BAF (open squares). At the indicated times after NGF deprivation, NGF was added back to the cultures for 7 d. The number of NGF-rescued cells was quantitated by crystal violet staining and counting all stained cells in the culture dish. Data showing time course of loss of cytochrome c and Mitotracker staining are taken from Fig. 3 C. Results are mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. Bar, 20 μm.