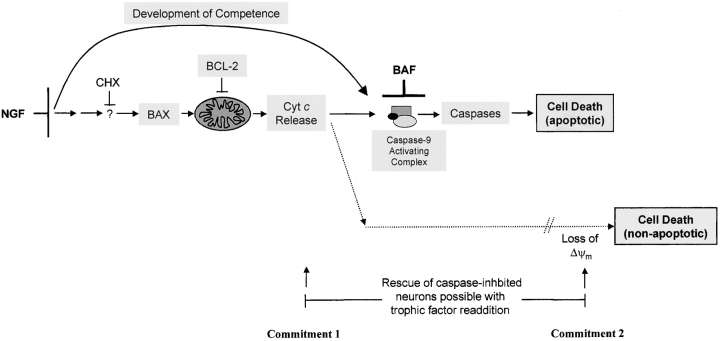
Figure 7.
Sympathetic neuronal death induced by NGF deprivation. Sequence of events occurring after NGF deprivation in sympathetic neurons. Cycloheximide (CHX) inhibits an upstream event that leads to the translocation of BAX to the mitochondria and the subsequent release of cytochrome c (Cyt c) from the mitochondria. Cytosolic cytochrome c presumably activates caspase-9 and induces cell death. Cytochrome c–mediated activation of caspases also requires the NGF deprivation–induced development of competence. Loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) occurs subsequent to loss of cytochrome c. If caspases are inhibited, rescue of the NGF-deprived, caspase-inhibited neurons is possible with NGF readdition even after the point of cytochrome c release, but not beyond the point of loss of mitochondrial membrane potential.