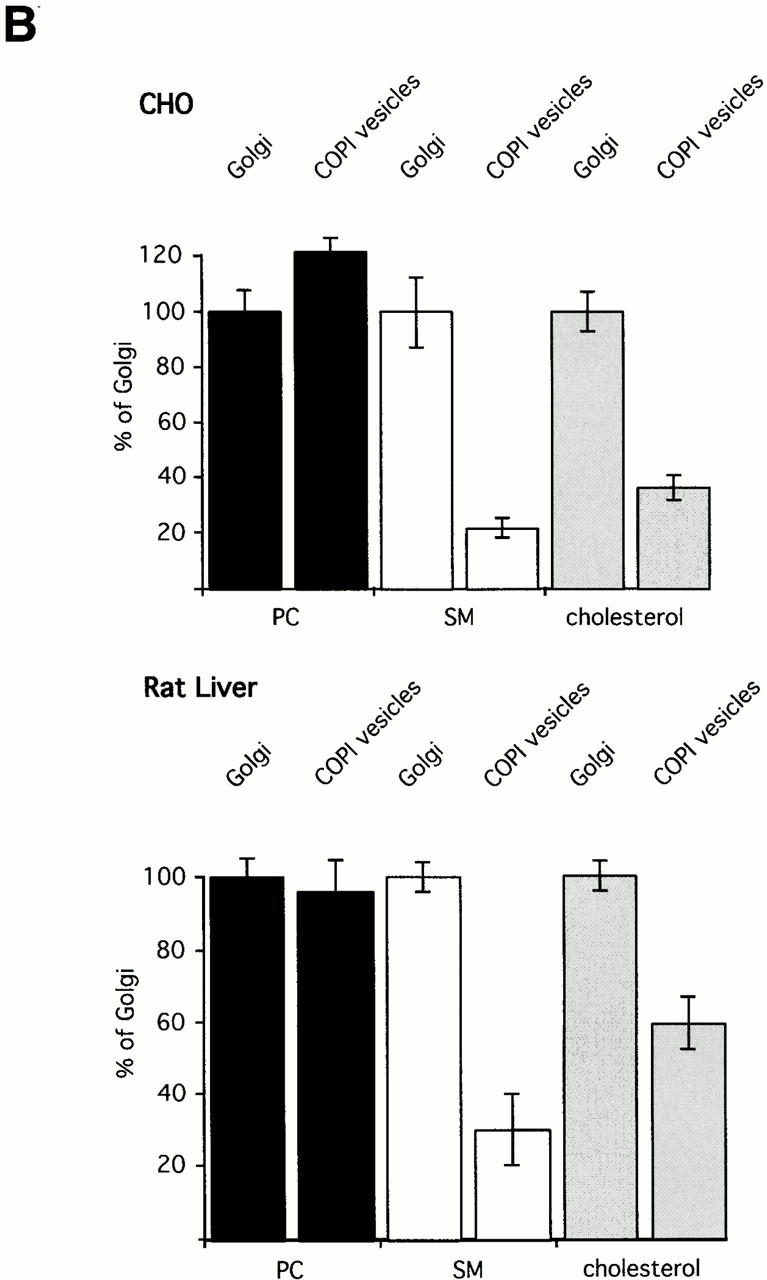
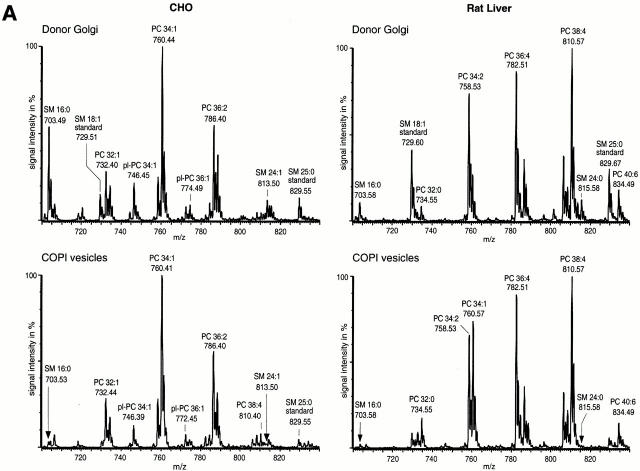
Figure 3.
(A) Mass spectrometric analysis of donor Golgi membranes and Golgi-derived COPI-coated vesicles. Golgi membranes were isolated from either CHO cells or rat liver and incubated with bovine brain cytosol, ATP-regenerating system, and GTPγS. Vesicles were purified on an isopycnic sucrose gradient. As described in Materials and Methods, lipids from donor Golgi membranes and COPI vesicles were extracted in the presence of internal PC and SM standards. PC and SM quantification was performed in PREC 184 mode. The top panels show PREC 184 spectra of CHO (left) and rat liver (right) donor Golgi membranes. The bottom panels show the corresponding PREC 184 spectra of COPI vesicles generated from CHO (left) and rat liver (right) Golgi membranes. Each spectrum shown was averaged from 100 separate scans, each of 4-s duration. The molecular masses in daltons, the corresponding numbers of total carbon (C) atoms in both fatty acids, and the numbers of double bonds (Σ C atoms:Σ of double bonds) are given for the major peaks. pl, plasmalogen. (B) Quantification of PC, SM, and cholesterol in donor Golgi and COPI vesicle fractions of CHO or rat liver membranes. Lipid quantification was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The results of quantification of PC (black bars), SM (white bars), and cholesterol (gray bars) in CHO (top) and in rat liver (bottom) membranes are shown. The amounts of PC, SM, and cholesterol in donor Golgi membranes are set to 100%. Results are shown as mean ± SD. Reference to absolute amounts of these lipids present in COPI vesicles and their parental membrane fractions is given in Table .