Figure 7.
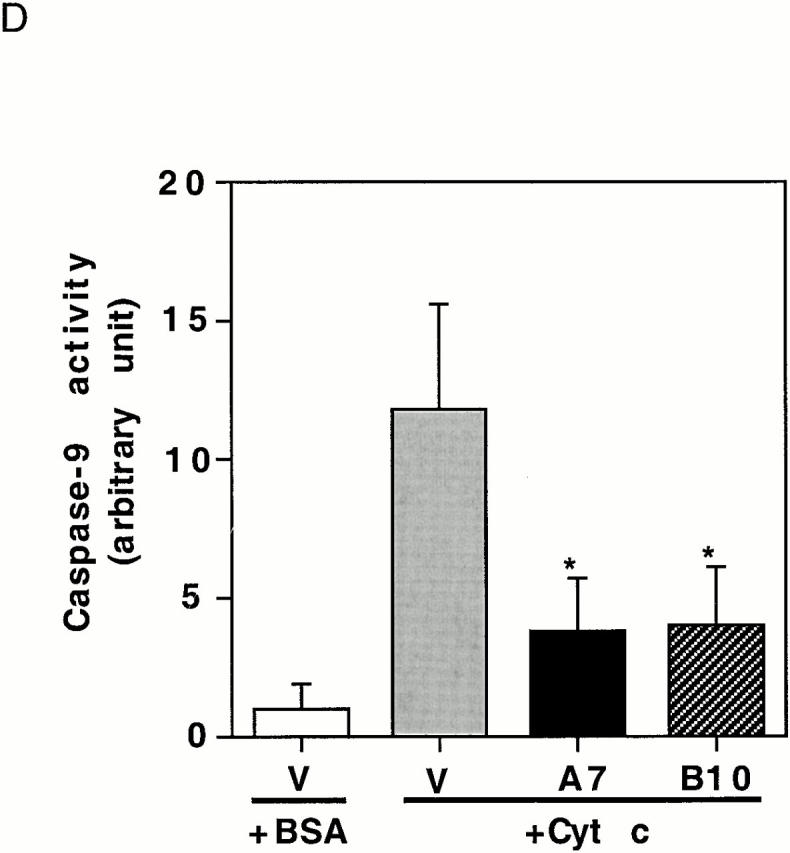
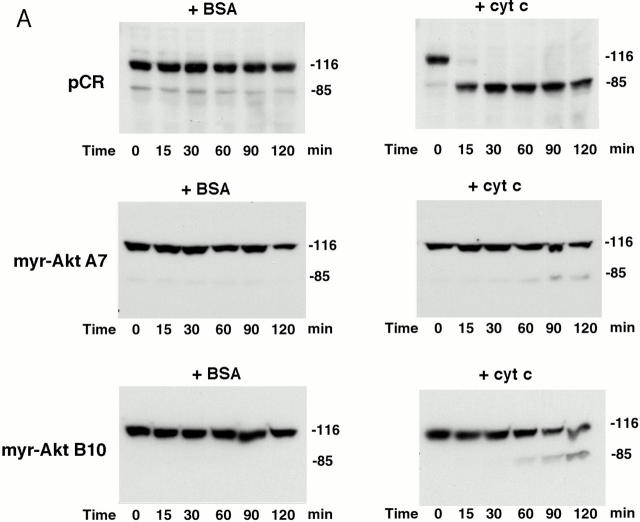
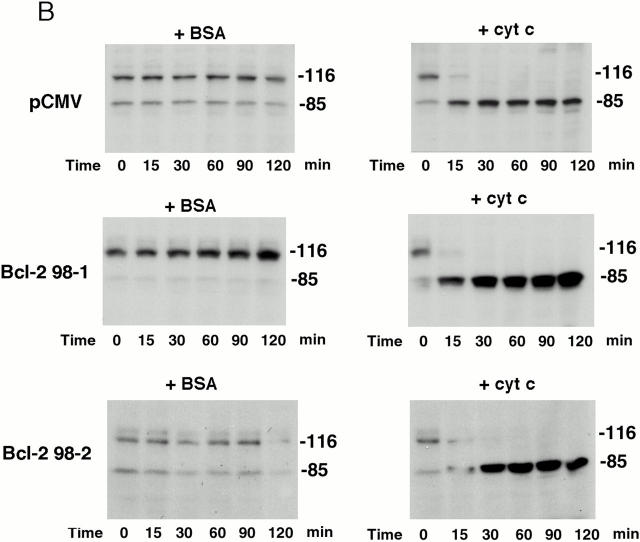
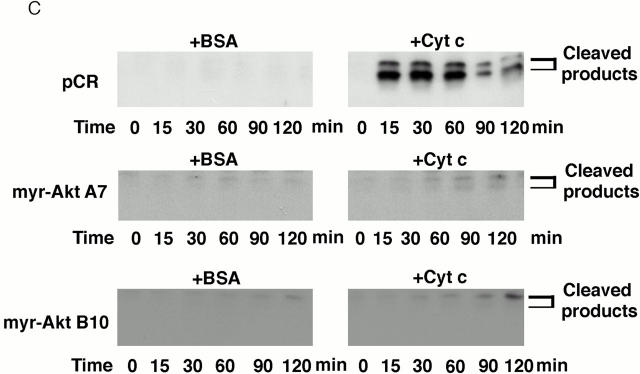
Active Akt but not Bcl-2 inhibits caspase activation induced by cytochrome c in a cell-free system. (A) Extracts from active Akt stable cell lines but not a vector control line inhibit cytochrome c–induced PARP cleavage. Cell-free assays were prepared as described in Materials and Methods and samples were taken at the indicated time. The blot was probed with an mAb against PARP. Note that the addition of cytochrome c induced rapid cleavage of intact PARP (116 kD) into the 85-kD fragment, whereas addition of BSA did not. PARP cleavage was markedly inhibited in lysates from two active Akt clones (A7, middle, and B10, bottom) compared with vector control (top). (B) Extracts from Bcl-2 stable cell lines do not inhibit cytochrome c–induced PARP cleavage. Cell-free assays were performed as described above for the indicated period. The blot was probed with an mAb against PARP. Note that addition of cytochrome c induced a similar degree of PARP cleavage in both vector control cells (top) and two Bcl-2 stable lines (98-1, middle, and 98-2, bottom). (C) Extracts from active Akt stable cell lines but not a vector control line inhibit cytochrome c–induced caspase-3 cleavage. Cell-free assays were performed as described above. The blots were probed with a polyclonal antibody selectively recognizing cleaved/activated caspase-3. Note that caspase-3 cleavage/activation was markedly inhibited in two active Akt clones (middle and bottom) compared with vector control (top). Cleaved products represent the 20- and 17-kD processed caspase-3. (D) Caspase-9 activity induced by cytochrome c is inhibited in cell extracts from two active Akt clones compared with vector control. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.01 by Student's t test.