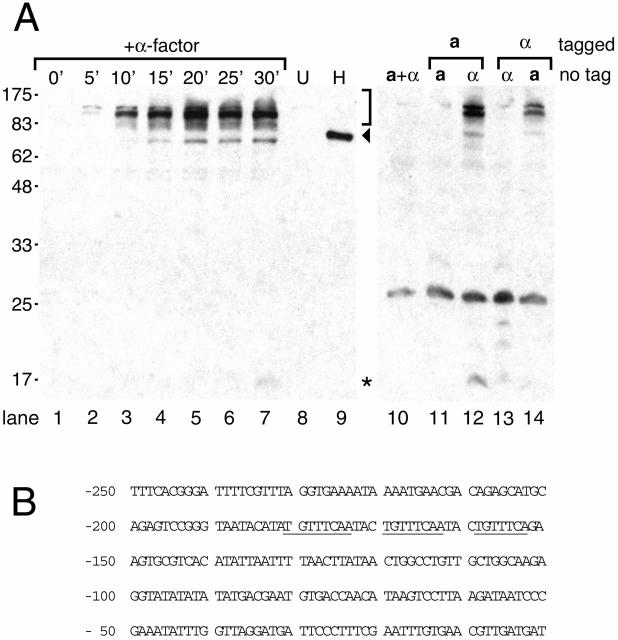
Figure 3.
Expression profiles of Prm1p. (A, lanes 1–9) A strain of mating type a bearing a chromosomal copy of PRM1-HA (lanes 1–7 and 9), or a wild-type control strain (lane 8) was treated with 10 μg/ml alpha factor for 0–30 min, pelleted, and lysed by bead beating. Extracts were resolved by SDS-PAGE on a 12.5% gel and immunoblotted using an anti–HA antibody. For lane 9, the extract was treated with endoglycosidase H before analysis by SDS-PAGE. (A, lanes 10–14) The following strains were mixed: control wild-type strains of mating types a and α (A, lane 10), an a strain bearing PRM1-HA and an untagged strain of the same (A, lane 11) or the opposite (A, lane 12) mating type, an α strain bearing PRM1-HA and an untagged strain of the same (A, lane 13) or the opposite (A, lane 14) mating type. These mixtures were rotated for 30 min at 30°C, pelleted, lysed, and the extracts were analyzed as above. The 73-kD form of Prm1p, presumably corresponding to the primary, unglycosylated translation product, is indicated with the arrowhead. The glycosylated forms of Prm1p migrating as a broad band centered at 115 kD are indicated with the bracket. A 15-kD putative proteolytic fragment is indicated with the asterisk. (B) The PRM1 promoter sequence, beginning 250 nucleotides upstream of the translational start codon, is shown. Pheromone response element consensus sequences are underlined.