Fig. 4. Disruption of aggregation of SEMs hinders C. parvum attachment to and entry of cholangiocytes. H69 cells treated with pharmacological agents known to disrupt SEMs or siRNA to ASM were exposed to C. parvum for 2 h followed by immunofluorescent microscopy.
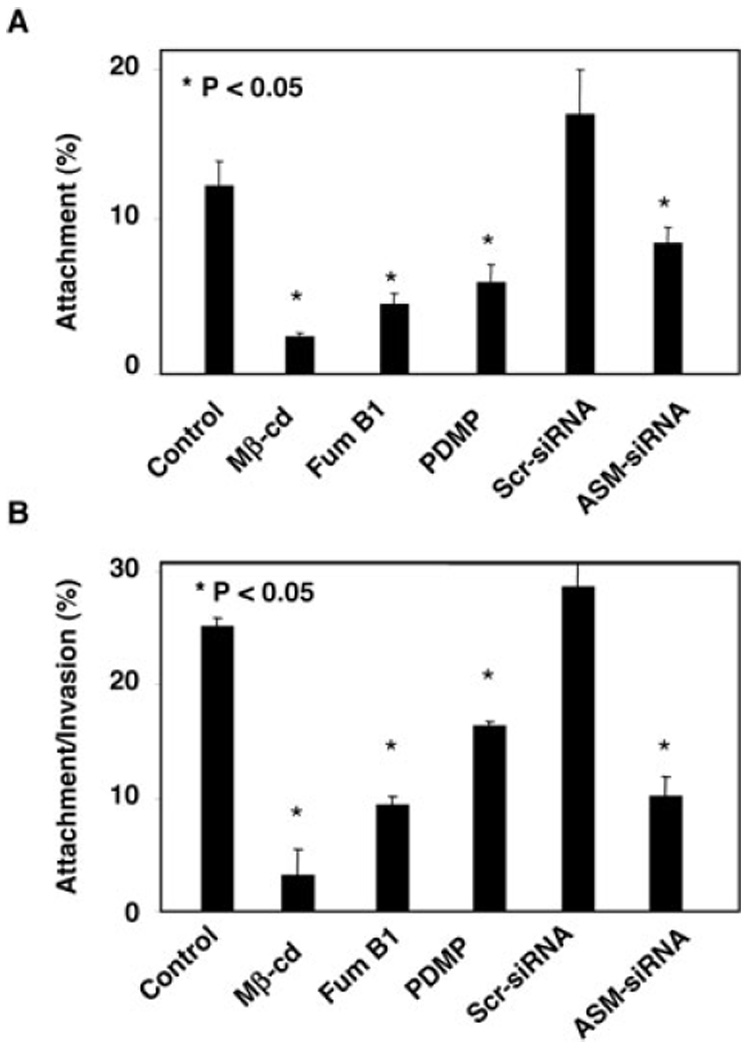
A. Attachment assay in prefixed cells. Cells treated with methyl-β-cyclodextrin (Mβ-cd), Fumonocin B1 (Fum B1), PDMP or ASM-siRNA each showed a significant decrease of C. parvum attachment to host cells.
B. Attachment/invasion assay in non-fixed cells. Cells treated with Mβ-cd, Fum B1, PDMP or ASM-siRNA each showed a significant decrease of C. parvum attachment/invasion rate. Scr-siRNA, scrambled siRNA.
