Figure 1.
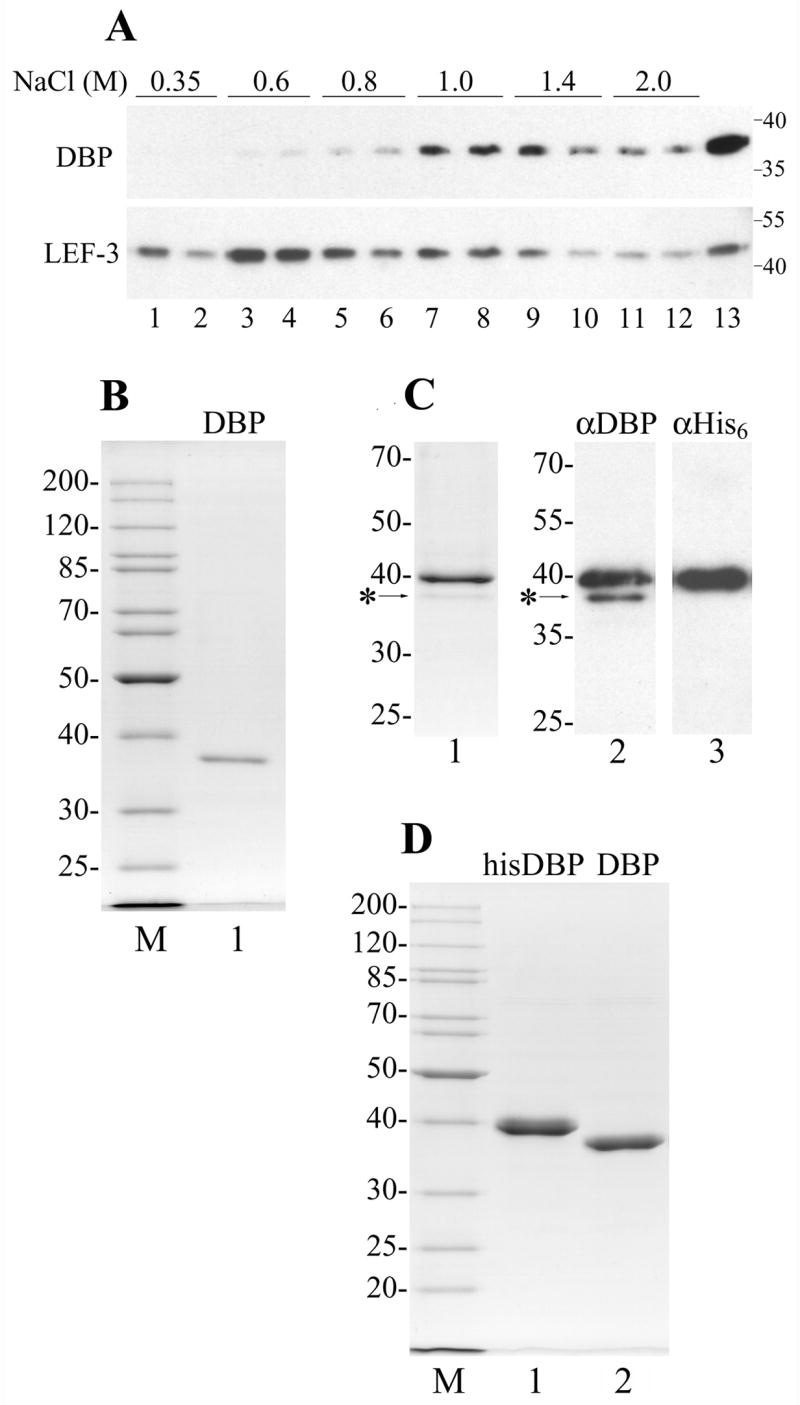
Purification of AcMNPV DBP. (A) Chromatin was obtained from 3 × 107 cells infected with AcMNPV at 20 hpi and was sequentially extracted with buffers containing NaCl as indicated. Each extraction step was repeated twice. Lane 13 shows the residue after the chromatin extraction with salt. After precipitation of insoluble material, the supernatants were subjected to SDS-11% PAGE followed by Western blotting with polyclonal antibodies to DBP and LEF-3. The molecular weight standards (in kDa) are shown on the right. (B) DBP was purified from the cytoplasm of Sf9 cells infected with wild type AcMNPV by column chromatography on ssDNA-cellulose and DEAE-Toyopearl. 230 ng were subjected to SDS-10% PAGE followed by Coomassie staining (lane 1). (C), Copurification of his-tagged DBP with wild type DBP. Lane 1, 400 ng of his-tagged DBP purified by chromatography on Ni-NTA column was subjected to SDS-11% PAGE followed by Coomassie staining. Lanes 2 and 3, 80 ng of the his-tagged DBP was subjected to SDS-10% PAGE followed by Western blotting with polyclonal antibodies to DBP (lane 2) or with monoclonal antibodies to His6 (lane 3). The position of wild type DBP is indicated by the asterisk. (D) The his-tagged DBP was purified from Sf9 cells infected with the recombinant virus vAcHisDBP by column chromatography on Ni-NTA agarose and DEAE-Toyopearl. 1.96 μg of the his-tagged DBP (lane 1) and 1.6 μg of the his-tagged DBP treated with AcTEV protease (lane 2) were subjected to SDS-11% PAGE. Lanes M in panels B and D show molecular weight standards.
