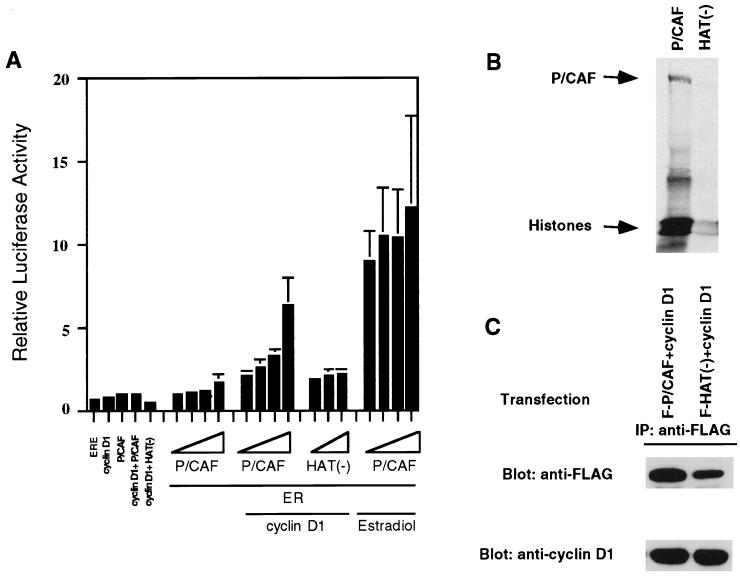
Figure 3.
Potentiation of cyclin D1-stimulated ER activity by wild-type P/CAF, but not by a mutant derivative that lacks HAT activity. (A) SAOS-2 cells were transfected with the reporter plasmids p(ERE)2-TATA-luc (0.25 μg), pCMV-β-galactosidase (0.5 μg), and expression plasmids encoding the ER (50 ng), cyclin D1 (0 or 1.0 μg), plus FLAG-P/CAF or HAT(−) (0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, or 2.0 μg). To assess the effects of cyclin D1, P/CAF, and HAT(−) on the reporter in the absence of the ER, 2 μg of each coactivator was used. The respective empty vectors were used to make up a total of 3 μg DNA in each transfection. Where indicated, the cells were treated with estradiol (10 nM) for 24 hr. The fold activation is calculated relative to that of the ER alone, which is set to 1. The graph shows the averages + SEs from three independent experiments, each of which was done in duplicate. (B) Acetyl-transferase activity of P/CAF and the HAT(−) mutant. Immunoprecipitations using an anti-FLAG antibody were performed on lysates from COS cells transfected with plasmids encoding FLAG-tagged P/CAF or the HAT(−) mutant derivative. The precipitated proteins then were incubated with histones in the presence of 14C-acetyl-CoA. Proteins were resolved by SDS/PAGE in a composite gel cast, with 15% acrylamide in the lower half and 10% acrylamide in the upper half, and subsequently transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane and exposed to film for 48 hr. (C) The association between cyclin D1 and P/CAF or the HAT(−) derivative. Immunoprecipitations were carried out with anti-FLAG antibodies on lysates from COS cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. Precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting for their cyclin D1 and FLAG-P/CAF content.