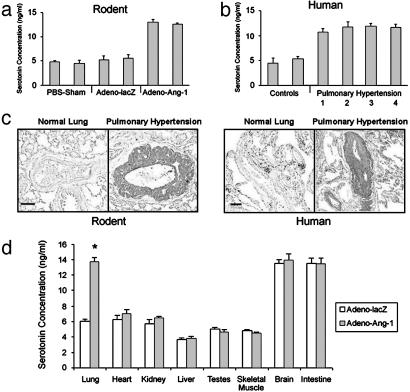
Fig. 5.
High levels of serotonin in rodent and human pulmonary hypertensive lung tissue. (a) ELISA quantitation of serotonin in lungs from animals injected with Adeno-Ang-1 (pulmonary hypertension group) compared with serotonin levels in lungs from rodents injected with Adeno-lacZ or PBS (normotensive control groups). (b) ELISA quantitation of serotonin in lung samples taken from humans with pulmonary hypertension resulting from chronic thromboembolism (bar 1), pulmonary overcirulation from ventricular septal defects (bar 2), scleroderma (bar 3), and idiopathic nonfamilial disease (bar 4), compared with lung specimens obtained from patients without pulmonary hypertension (controls). (c) Immunohistochemical staining of lung tissue with anti-serotonin antibody shows that rodents with Ang-1-induced pulmonary hypertension have serotonin within the vascular wall of pulmonary vessels ≤500 μm in diameter (Left), whereas serotonin staining is not detected in normal rat lung tissue. Human tissue stained with anti-serotonin antibody demonstrates serotonin in the wall of small pulmonary vessels in pulmonary hypertensive lung tissue only (Right), without staining in lung specimens from patients without pulmonary hypertension. (Scale bars represent 50 μm.) (d) ELISA quantitation of serotonin in organs of animals with pulmonary hypertension induced by Adeno-Ang-1, compared with animals without pulmonary hypertension injected with control Adeno-lacZ virus. *, P < 0.01 compared with lung control group.