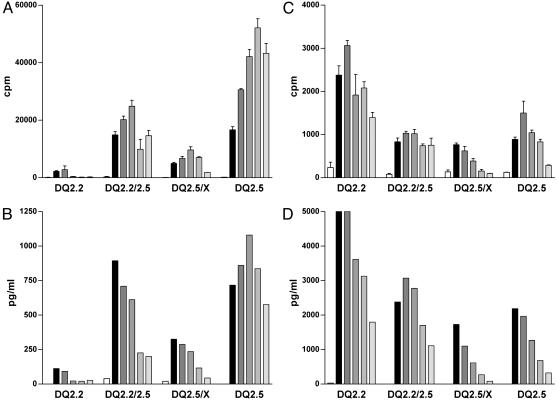
Fig. 1.
Gene dose effect in stimulation of gluten-specific T cell clones. Stimulation of two gluten-specific T cell clones with the gluten epitopes glia-α9(A and B) and glt-17 (C and D) is shown. Five concentrations of the epitopes were tested in the range from 0.2 μg/ml (light-gray bars) to 20 μg/ml (black bars). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of various HLA-DQ2+ healthy individuals were used as APC (x axis). The epitopes were tested as deamidated peptides. T cell stimulation was determined by measurement of proliferation (A and C) and IFN-γ production (B and D). Production of tumor necrosis factor α, IL-10, IL-5, and IL-4 correlated with the levels of IFN-γ secreted (data not shown). The percentage of HLA class II-expressing cells in the PBMCs was determined by FACS analysis and was similar for each donor (data not shown). These results are representative of three independent experiments using PBMCs from various donors.