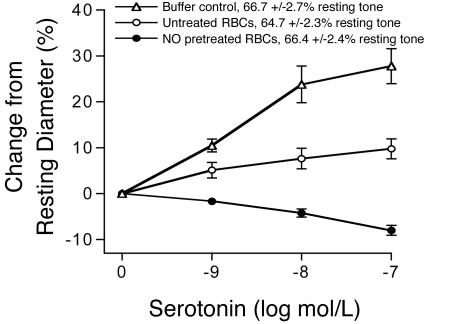
Fig. 3.
The bioactivity of 5-HT was converted from vasodilation to vasoconstriction by RBCs treated under hypoxia with NO. Addition of 5-HT to isolated porcine arterioles containing buffer alone resulted in dose-dependent vasodilation (n = 9). The addition of untreated RBCs to the lumen of the arteriole attenuated 5-HT-induced vasodilation, suggesting that some 5-HT-induced NO is consumed by RBCs (n = 5). Addition of 5-HT to arterioles containing NO-pretreated RBCs resulted in vasoconstriction, suggesting that these RBCs consumed NO more rapidly than untreated RBCs (n = 5). The resting tone of the arterioles did not differ with the addition of untreated or NO-pretreated hypoxic RBCs to the vessel lumen, suggesting that lysis was minimal and no export of vasodilatory or vasoconstrictive species occurred.