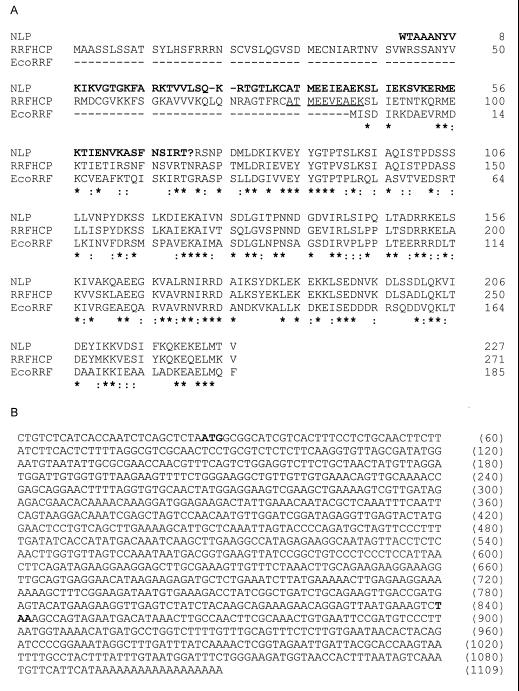
Figure 1.
(A) Amino acid sequence of RRFHCP and NLP (from carrot) in comparison with E. coli RRF sequence (EcoRRF). The NLP amino acid sequence is not deduced from the original sequence (GenBank accession no. X72384) but from a corrected sequence in which 1 nt (G216) has been removed. The modified residues are represented in bold and as a “?”. Two gaps (–) have been inserted in the NH2-terminal part of the NLP sequence. The NH2-terminal sequence of mature RRFHCP (10 residues, underlined letters) was determined by sequencing of mature RRFHCP from spinach chloroplasts. Identical (∗) and similar (two dots) residues are indicated. Conservative amino acid substitutions were grouped as follows: I-L-M-V, K-R-H, A-S-P-T-G, Y-F-W, N-Q, and D-E. (B) DNA sequence of RRFHCP cDNA. The initiation (ATG) and the termination (TAA) codons are in bold.