Abstract
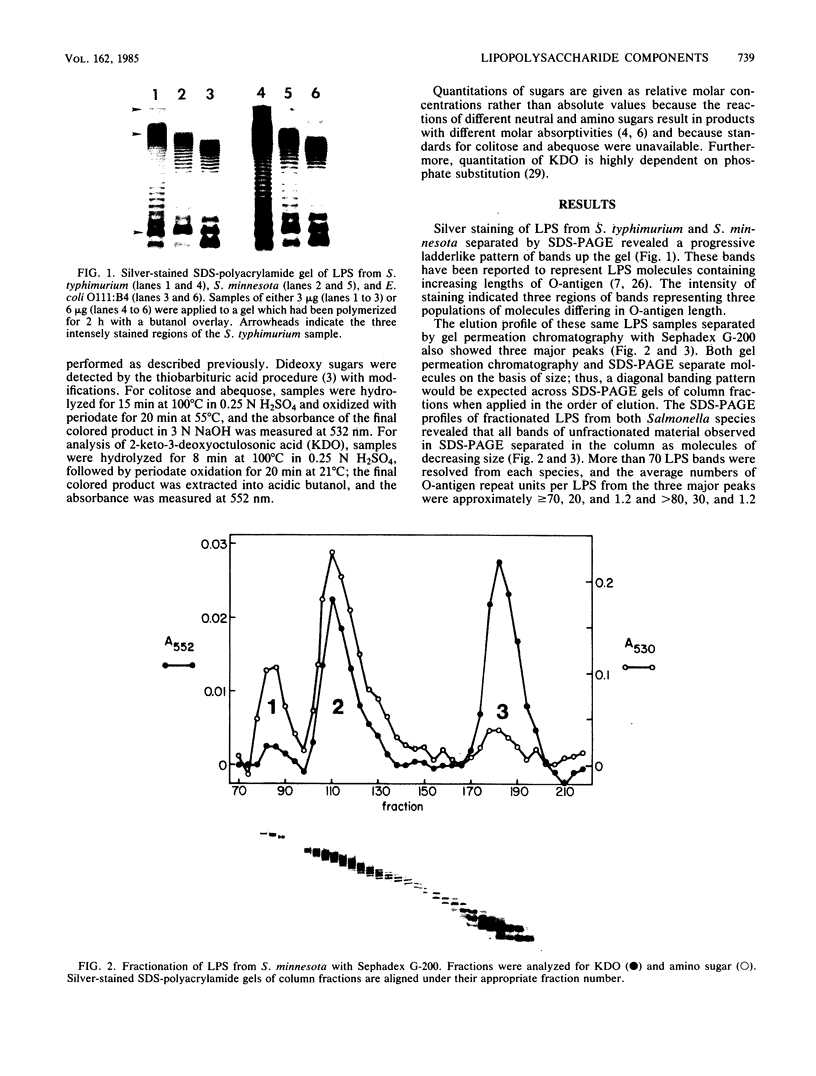
Lipopolysaccharide from smooth strains of Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella minnesota, and Escherichia coli O111:B4, O55:B5, and O127:B8 was fractionated by gel filtration chromatography. All lipopolysaccharide samples separated into three major populations. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the fractions from S. typhimurium and S. minnesota indicated that the three peaks were made up of molecules with average O-antigen lengths of (i) 70 or more repeat units, (ii) 30 and 20 repeats units in the samples from S. typhimurium and S. minnesota, respectively, and (iii) 1 repeat unit. In contrast to the Salmonella samples, peak 1 from the E. coli samples was not detected on polyacrylamide gels and lacked detectable phosphate. This high-molecular-weight material had a sugar composition similar to that of O-antigen and was tentatively identified as capsular polysaccharide. Peaks 2 and 3 of the E. coli samples were analogous to those of the Salmonella isolates, containing lipopolysaccharide molecules with averages of 18 and 1 O-antigen repeat units, respectively. These lipopolysaccharide molecules did not completely dissociate during electrophoresis, and multimers were detected as distinct, anomalous, slow-migrating bands. Increasing the concentration of sodium dodecyl sulfate in the gels resulted in the dissociation of these multimers.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bezard G. A highly sensitive periodic acid-silver stain for 1,2-diol groups of glycoproteins and polysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt R., Berman E. R. A rapid procedure for the estimation of amino sugars on a micro scale. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., White D., Orskov F., Orskov I., Rick P. D., Lewis M. S., Bhattacharjee A. K., Leive L. A surface polysaccharide of Escherichia coli O111 contains O-antigen and inhibits agglutination of cells by O-antiserum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1210–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1210-1221.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman N., Leive L. Complement activation via the alternative pathway by purified Salmonella lipopolysaccharide is affected by its structure but not its O-antigen length. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):376–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J. Aberrant migration of lipopolysaccharide in sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):685–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert R. E., Hurlbert I. M. Biological and physicochemical properties of the lipopolysaccharide of Chromatium vinosum. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):983–994. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.983-994.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Schmetz M. A., Goldman R. C., Leive L., Frank M. M. Mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing: inserted C5b-9 correlates with killing for Escherichia coli O111B4 varying in O-antigen capsule and O-polysaccharide coverage of lipid A core oligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):113–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.113-117.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Söderholm E., Bundle D. R., Griffith D. W. Structural studies of the O-antigens from Salmonella greenside and Salmonella adelaide. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Jan 1;111(2):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg B., Lindh F., Lönngren J. Structural studies of the O-specific side-chain of the lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli O 55. Carbohydr Res. 1981 Nov 2;97(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)80528-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Structural and antigenic heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.210-216.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Risse H. J., Ruschmann E., Schlecht S., Schmidt G., Schulte-Holthausen H., Wheat R., Westphal O., Schlosshardt J. Structural relationship of Salmonella O and R antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):349–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Leive L. Fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli O111:B4 prepared by two extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2911–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Rick P. D. Size heterogeneity of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides in outer membranes and culture supernatant membrane fragments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.630-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reske K., Jann K. The O8 antigen of Escherichia coli. Structure of the polysaccharide chain. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):320–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Chun P. W. The dispersion of gram-negative lipopolysaccharide by deoxycholate. Subunit molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1221–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vukajlovich S. W., Morrison D. C. Conversion of lipopolysaccharides to molecular aggregates with reduced subunit heterogeneity: demonstration of LPS-responsiveness in "endotoxin-unresponsive" C3H/HeJ splenocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2804–2808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Morrison D. C. Evidence for different requirements in physical state for the interaction of lipopolysaccharides with the classical and alternative pathways of complement. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov;128(1):137–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









