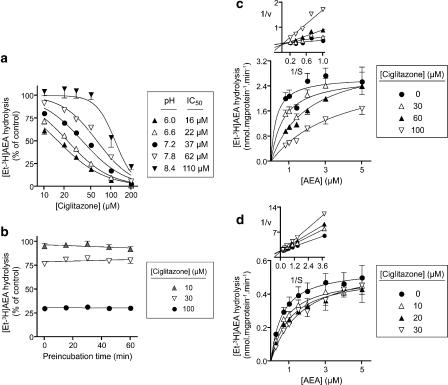
Figure 2.
Interaction of ciglitazone with FAAH in rat brain membrane fractions. (a) Effect of ciglitazone upon the hydrolysis of 0.5 μM [3H-Et]AEA over the pH range 6.0–8.4. The protein contents were 3.0, 2.1, 1.5, 1.1 and 0.8 μg per assay at pH 6.0, 6.6, 7.2, 7.8 and 8.4, respectively, the differences reflecting the pH optimum of the enzyme (Schmid et al., 1985). Preincubation times were 10 min. In (b), ciglitazone was preincubated for different times before addition of 2 μM [3H-Et]AEA (assay pH 7.4). In (c) and (d), no preincubation phase was used and the pH of the assay buffer was either 7.4 ((c) 1.5 μg protein per assay) or 6.0 ((d) 2 μg protein per assay). In (a–c), the incubation times with [3H-Et]AEA were 5 min, and in (d) it was 10 min. Data are means±s.e.m., n=3. The insets to (c and d) illustrate the competitive nature of the inhibition. AEA, anandamide (arachidonoylethanolamide); FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase.