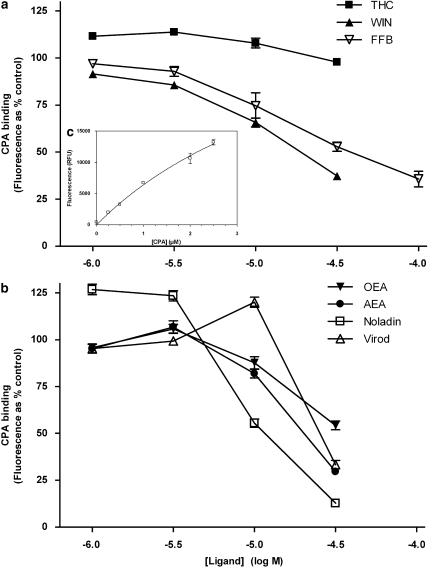
Figure 1.
Binding of cis-parinaric acid (CPA) to mPPARα (GST fusion mouse PPARα ligand-binding domain). Concentration-dependent inhibition of CPA (2 μM) binding to mPPARα (1 μM) in the presence of selected synthetic (a) and endogenous (b) compounds. The inset c shows the concentration dependence of specific CPA binding (fluorescence in the presence of mPPARα−the fluorescence in the absence of mPPARα). Data are means±s.e.mean of three experiments conducted in quadruplicate and are expressed as % CPA-derived fluorescence in the absence of competing ligand (a and b) or as relative fluorescence units (c). PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.