Fig. 5.
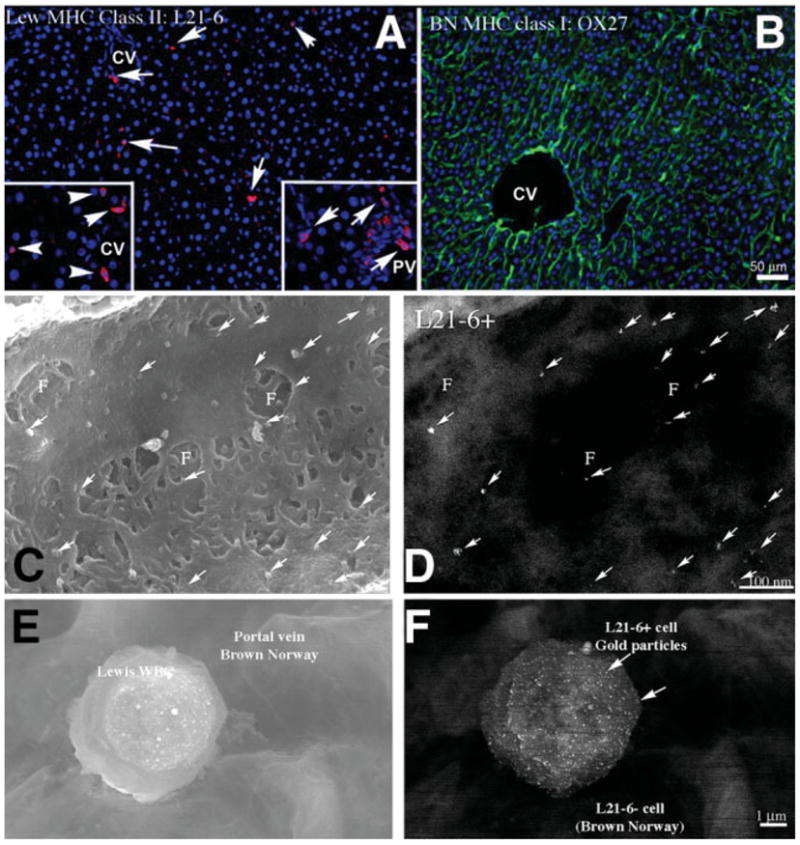
Evaluation of recipient LEW cells in BN liver. (A) LEW-specific MHC class II antibody (L21-6) identified LEW cells in the BN donor liver 3 days post-OLTx. Few cells are observed in the sinusoids of the liver (red, arrows), and these cells do not show the flattened shape typical of LSECs. Higher concentrations of L21-6+ cells are found in perivascular areas surrounding the central vein (CV, left insert, arrowheads) and in the portal triad (PV, right insert, arrows) but are not integrated into the large vessel intima. (B) Control. BN MHC class I staining of most cell membranes in the transplanted BN rat liver is shown (green). High-resolution immuno-SEM evaluation of an engrafted LSEC of recipient origin was then undertaken. (C) Secondary electron image and (D) parallel backscattered electron image identify the recipient-specific surface marker L21-6 (arrows, 15-nm gold particles) on the surface of a fenestrated LSEC in the BN donor liver sinusoid. Gold particles are on the LSEC, not under the fenestrations. This positive result was seen in 1 out of several hundred cells examined using this technique, indicating it is an uncommon event. (E, F) Secondary electron image and parallel backscattered electron image, respectively, of the typical shape of an L21-6 positive cell in the liver vasculature. This cell is most likely a leukocyte.
