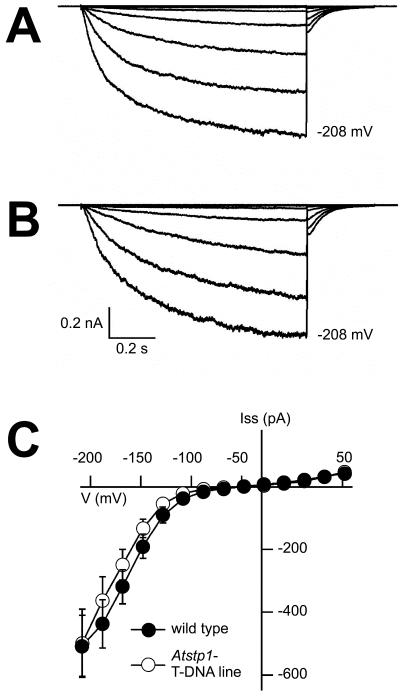
Figure 7.
Electrophysiological analyses of macroscopic K+ currents in Arabidopsis guard cell protoplasts. Voltage- and time-dependent properties of inward K+ currents in guard cell protoplasts from an AtSTP1 WT plant (A) and from the Atstp1 T-DNA insertion mutant (B). Voltage pulses were applied to the protoplasts in the whole-cell configuration starting from a holding potential –48 mV in 20-mV decrements from +52 to –208 mV. Pipette solution contained 150 mm potassium gluconate, 2 mm MgCl2, 10 mm EGTA, 2 mm Mg-ATP, and 10 mm HEPES/Tris (pH 7.4). External solution contained 30 mm potassium gluconate, 1 mm CaCl2, and 10 mm MES/Tris (pH 5.6). C, Voltage dependence of inward K+ currents in guard cell protoplasts from WT (n = 13) and AtSTP1 knockout plants (n = 14). Current amplitudes were sampled at the end of 1-s pulses to voltages in the range from +52 to –208 mV. External solution contained 20 mm CaCl2, 30 mm potassium gluconate, and 10 mm MES/Tris (pH 5.6). Data points represent means ± se.