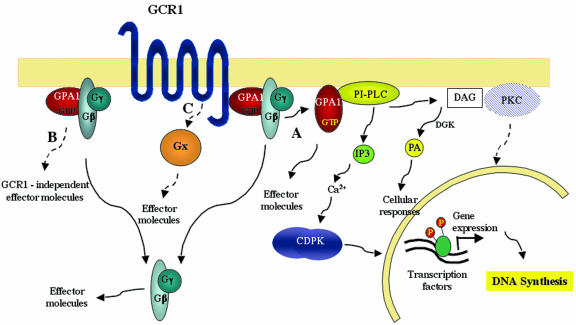
Figure 8.
Speculative model showing how GCR1 signaling may lead to DNA synthesis. Three different signaling pathways are shown. A, GCR1 stimulates PI-PLC activity through the activation of GPA1. Upon GCR1/GPA1 activation, PI-PLC produces IP3 and DAG. The scheme shows direct activation of PI-PLC by GPA1, but such activation could also be indirect. In addition, GPA1 may have other effectors not shown here. Whereas IP3 mediates the activation of CDPK, through Ca2+ level increases, DAG is immediately converted by a DAG kinase (DGK) into PA, which can in turn mediate other cellular responses. Once activated by Ca2+, CDPK regulates DNA synthesis through phosphorylation processes. PKC, activated by DAG, may also play a role in the regulation of DNA synthesis. B, Independent of GCR1, GPA1 may initiate other signaling pathways, as has been found in animal cells. C, GCR1, interacting with other GTP-binding proteins, may activate different effector molecules (these may also include PI-PLC) and therefore trigger different cellular responses. The dashed arrows represent putative pathways that have not been demonstrated to date in plants.