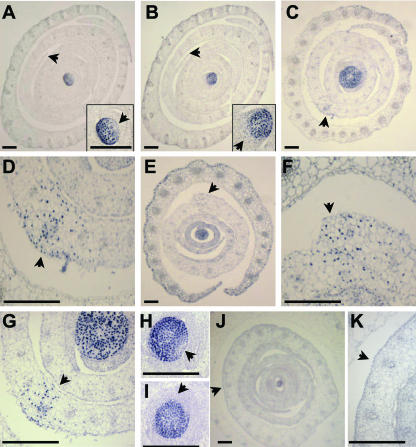
Figure 6.
NPA-induced fused margins accumulate ectopic KNOX protein. KNOX immunolocalization of transverse sections of maize shoots cultured without NPA (A–C) and with NPA (D--G). KNOX proteins accumulate in the SAM and are down-regulated in the leaf founder cells of the P0 (arrow in inset A); a larger area of down-regulation is seen in the developing P1 leaf (arrow in inset B). Ectopic KNOX accumulation is seen in the fused margin domains of the P4 leaves in NPA-treated shoots (arrows in C–G). C and close-up in D, From a sample sectioned at the level of the second leaf. Closer to the tip of the SAM (E and close-up in F), the fused margins of an NPA-treated sample begin to separate, although the margins are thicker than in untreated samples (A and B), and KNOX accumulation is retained (F). G is another sample taken at the P2 level. When NPA-treated samples are switched to NPA-free culture for 20 d, normal down-regulation of KNOX protein at the P0 (H) and P1 (I) domains is correlated with resumption of leaf initiation. Fusion of the margins in the fourth leaf is retained after samples are switched to NPA-free culture (J), although ectopic KNOX accumulation does not persist (close-up in I). P, Plastochron number. Bars in A to C, E, and J = 100 μm. Bars in D, F, G, H, I, K, and insets in A and B = 250 μm.