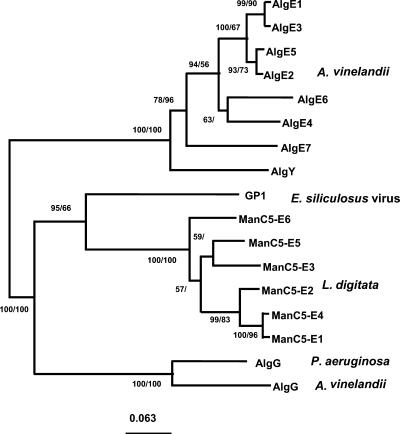
Figure 6.
Phylogeny of mannuronan C-5-epimerases. The topology shown here is the tree obtained using the neighbor-joining method (Jukes and Cantor distance correction), with 107 amino acids used in the analyses. Scale bar, Expected number of changes per sequence position. Numbers at the nodes refer to the bootstrap values (100 replicates) in distance and maximum-parsimony analyses, respectively. Absence of data indicates that the node was not totally reliable. The sequences used in the phylogenetic analysis are mannuronan C-5-epimerases from A. vinelandii: AlgE1 (TrEMBL no. Q44494), AlgE2 (TrEMBL no. Q44495), AlgE3 (TrEMBL no. Q44496), AlgE4 (TrEMBL no. Q44493), AlgE5 (TrEMBL no. Q44492), AlgE6 (TrEMBL no. Q9ZFH0), AlgE7 (TrEMBL no. Q9ZFG9), AlgY (TrEMBL no. Q9ZFG8), and AlgG (TrEMBL no. P70805); from P. aeruginosa: AlgG (TrEMBL no. Q51371); the GP1 coat protein from E. siliculosus virus, EsV-1 GP1 (TrEMBL no. Q8QN64); and the mannuronan C-5-epimerases identified in this study, ManC5-E1–6 (GenBank accession no. AJ496449–54).