Figure 8.
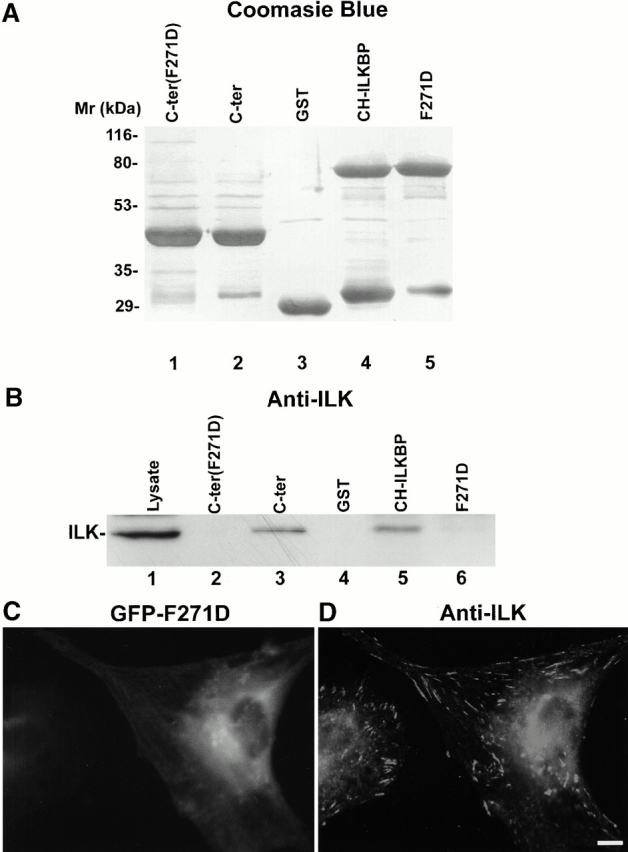
A point mutation that disrupts the ILK binding impairs the FA localization of CH-ILKBP. (A) GST–CH-ILKBP proteins. GST fusion proteins containing the mutant form (F271D) of CH2 domain (residues 258–372) (lane 1), the CH2 domain (residues 258–372) (lane 2), CH-ILKBP (lane 4), and the F271D point mutant (lane 5) and GST (lane 3) were separated on SDS-PAGE (10 μg/lane) and detected by Coomassie blue R-250 staining. (B) ILK binding. C2C12 cell lysates (260 μg) were incubated and precipitated with equal amount (10 μg) of GST or GST–CH-ILKBP proteins as indicated. ILK was detected by Western blotting with anti-ILK antibody 65.1. Lane 1 was loaded with C2C12 cell lysates (9 μg/lane). (C and D) FA localization. Rat mesangial cells expressing GFP fusion protein containing the full-length F271D point mutant were plated on fibronectin-coated coverslips and stained with anti-ILK antibody 65.1 and Rhodamine red™-conjugated anti–mouse IgG antibody. GFP-F271D (C) and ILK (D) were visualized under a fluorescence microscope equipped with GFP and rhodamine filters. Bar, 5 μm.
