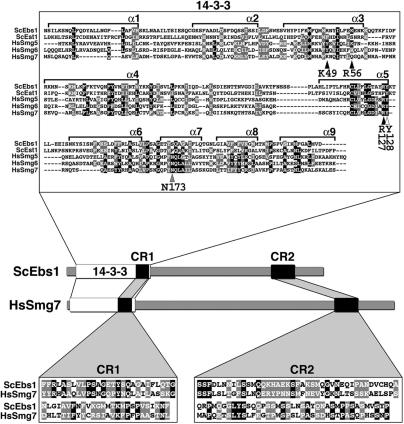
Figure 1.
The Smg5-7 14-3-3 phosphoserine-binding residues are conserved in Ebs1p. Multiple sequence alignment of the 14-3-3 domains of human Smg5 (amino acids 19–266), Smg6 (576–818) and Smg7 (1–236) proteins with the N-terminal regions of yeast Ebs1 (23–291) and Est1 (22–291) proteins. The alignment was produced using the ClustalW program. Alpha helices 1–9 (α1–α 9) are shown. Conserved amino acids are indicated as white letters on a black background while similar amino acids are white letters on a gray background. Arrowheads point to consensus 14-3-3 residues (indicated below each arrowhead) derived from the human 14-3-3 zeta isoform that have been implicated in phosphoserine binding for 14-3-3 domains across species. Black arrowheads indicate 14-3-3 residues that are conserved with respect to side-chain charge content in Ebs1p but not in Est1p, the white arrowhead points to a residue conserved in both Ebs1p and Est1p, the gray arrowhead highlights a residue, which is not conserved in either of the two yeast proteins. The cartoon depicts the domain architecture of yeast Ebs1 and human Smg7 proteins. Two conserved regions named CR1 and CR2 are indicated as black boxes and their sequence is shown in the lower insets. CR1: amino acids 231–283 in Ebs1p and 174–226 in Smg7; CR2: amino acids 710–789 in Ebs1p and 933–1013 in Smg7.