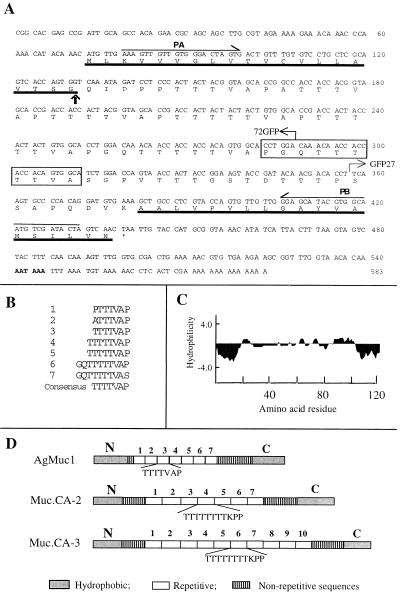
Figure 1.
Nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences of AgMuc1. (A) The N- and C-terminal hydrophobic protein domains are underlined. The putative cleavage site of the signal peptide is indicated by a vertical arrow and the borders of GFP fusion constructs by bent arrows. The putative polyadenylation signal sequence is in boldface. The polymorphic region missing in the Muc1b allele is boxed and the PCR primers used for genetic mapping (PA, PB) are indicated above the sequence. (B) The seven repeated motifs of the central protein core are aligned. The consensus repeat sequence is given at the bottom. (C) A Kyte–Doolittle hydropathy plot was generated with an average hydrophilicity window of 7 residues. (D) Diagrammatic comparison of the predicted amino acid sequence of the A. gambiae AgMuc1 mucin with that of Trypanosoma cruzi mucins, MUC.CA-2 and MUC.CA-3 (31, 32). AgMuc1 mucin contains TTTTVAP repeats, whereas the MUC.CA-2 and MUC.CA-3 mucins contain TTTTTTTTKPP motifs. All three mucins contain nonrepeated sequences between the repeat array and the N- and C-terminal hydrophobic sequences.