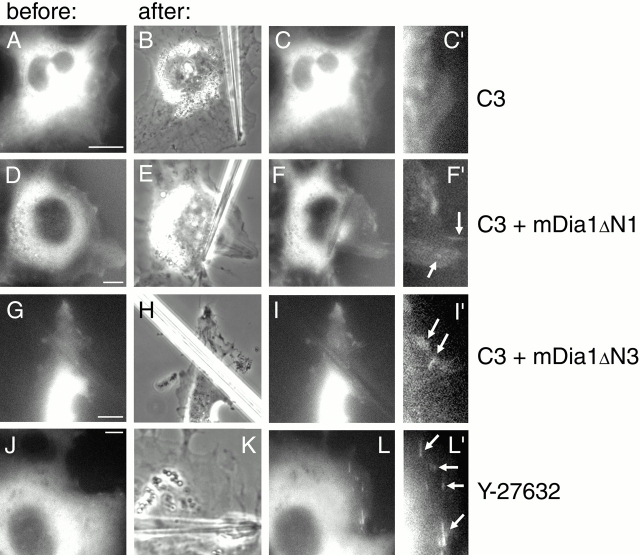
Figure 8.
Involvement of Rho, ROCK, and mDia1 in the force-induced formation of focal contacts. SV-80 cells were cotransfected with GFP–vinculin and C3 toxin (A–C′) or with GFP–vinculin, C3 toxin, and constitutively active mutants of mDia1, mDia1ΔN1 (D–F′) or mDia1ΔN3 (G–I′). Alternatively, the cells transfected with GFP–vinculin were treated with 10 μM ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 before application of force (J–L′). GFP–vinculin distributions in transfected cells several minutes before pipette shift are shown (A, D, G, and J). Positions of the pipettes, immediately after shift, are shown in phase images (B, E, H, and K). GFP–vinculin distributions in the cells 3–7 min after pipette shift are shown (C, F, I, and L). C′, F′, I′, and L′ represent enlarged parts of cells shown in C, F, I, and L, respectively. Newly formed focal contacts are indicated by arrows. Bars, 10 μm.