Figure 8.
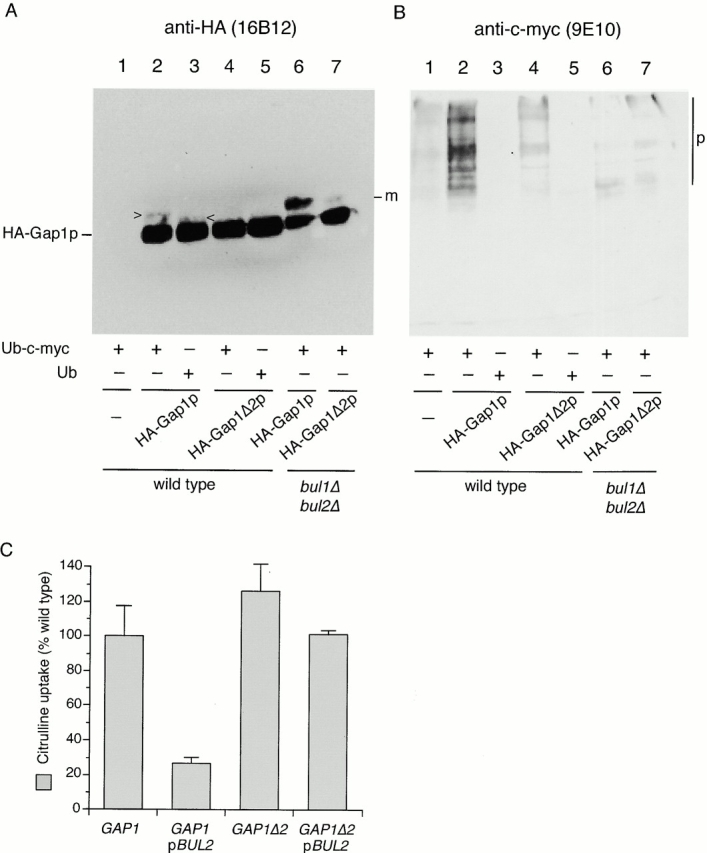
The Gap1Δ2p truncation is a poor substrate for Bulp-mediated polyubiquitination. (A) Wild-type (CKY703; lanes 1–5) and bul1Δ bul2Δ (CKY704; lanes 6 and 7) strains were transformed with combinations of empty vector (pRS316; lane 1), pHA-GAP1 (pCK235; lanes 2, 3, and 6), or pHA-GAP1Δ2 (pCK236; lanes 4, 5, and 7) and either pPCUP1-UBI-c-myc (pCK231; lanes 1, 2, 4, 6, and 7) or pPCUP1-UBI (pCK232; lanes 3 and 5). Strains were cultured overnight in minimal medium (SD Urea) at 24°C and CuSO4 was added to 0.1 μM to induce the CUP1 promoter 3 h before harvesting in exponential phase. Anti-HA (3F10) immunoprecipitates were subject to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with either (A) anti-HA (16B12) or (B) anti–c-myc (9E10). The following forms of Gap1p are marked: m, monoubiquitinated HA-Gap1(Δ2)p; p, polyubiquitinated HA-Gap1(Δ2)p; >, HA-Gap1p-Ub-c-myc; and <, HA-Gap1p-Ub. (C) A gap1::kanMX6 strain (CKY715) was transformed with combinations of plasmids carrying GAP1 (pCK233) or GAP1Δ2 (pCK234) and either a multicopy vector or one carrying BUL2 (pBUL2; pCK250) or the corresponding vector. Transformants were grown on minimal medium (SD Ammonia) at 24°C, and [14C]citrulline uptake activities were determined. Values are expressed as a percentage of the activity of the gap1Δ [pGAP1] strain. The data represents the mean for three separate transformants; error bars represent one standard deviation.
