Figure 4.
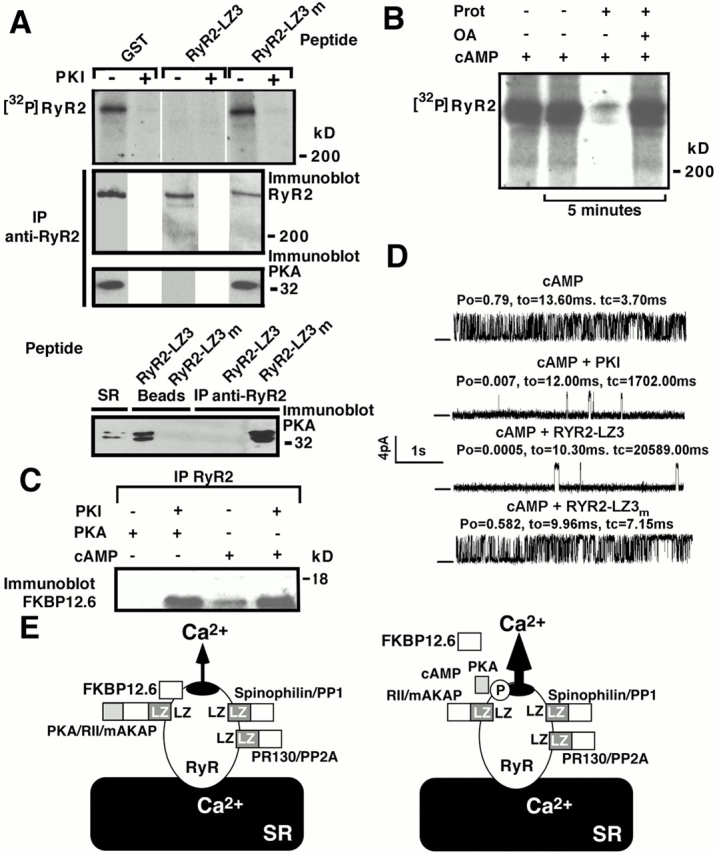
Kinase and phosphatases bound to RyR2 via LZ motifs regulate channel function. (A) Top panel: immunoprecipitated RyR2 was phosphorylated via activation of bound kinase by addition of cAMP (10 μM) and [γ-32P]ATP with or without PKI5–24 (500 nM). RyR2 phosphorylation by bound PKA was inhibited by preincubation with GST-RyR2-LZ3, but not by incubation with either GST alone or GST-RyR2-LZ3m (top panel). Equivalent amounts of RyR2 protein were present in each sample (second panel). Incubation with GST-RyR2-LZ3 but not with GST-RyR2-LZ3m disrupted binding of PKA to RyR2 (via mAKAP) as shown by coimmunoprecipitation (third panel). After incubation with GST-RyR2-LZ3, the PKA previously bound to RyR2 was now bound to GST-RyR-LZ3 beads and none was detected after coimmunoprecipitation with RyR2 (bottom panel). After incubation with RyR2–LZ3m, PKA coimmunoprecipitated with RyR2 and none was detected, by immunoblot, bound to the GST-RyR-LZ3m beads (bottom panel). “SR” denotes a sample of cardiac SR used as a positive control for the anti-PKA antibody. (B) RyR2-bound phosphatases dephosphorylate RyR2. Immunoprecipitated RyR2 was phosphorylated with cAMP for 15 min, and further phosphorylation was inhibited by PKI. RyR2 was dephosphorylated for 5 min by activation of bound phosphatases with protamine (Prot; 1 mg/ml), which was inhibited by okadaic acid (OA; 5 nM). (C) cAMP-induced activation of RyR2-bound PKA caused dissociation of FKBP12.6. (D) Pelleted membranes were introduced into planar lipid bilayers and RyR2 single channel properties determined. cAMP-induced phosphorylation of RyR2 by bound PKA increased P o. This was inhibited by the PKA inhibitor PKI. Preincubation with GST-RyR2-LZ3 (RYR2–LZ3) but not with GST-RyR2-LZ3m (RYR2–LZ3m) disrupted binding of PKA to RyR2 (see A) and inhibited the cAMP-dependent increase in channel P o. (E) Model of RyR2 macromolecular signaling complex, one subunit of the tetrameric RyR channel is shown. Targeting of kinases and phosphatases to RyR2 requires LZ interactions between RyR2 and targeting proteins. cAMP activates bound PKA, phosphorylating RyR2 and increasing calcium release.
