Figure 1.
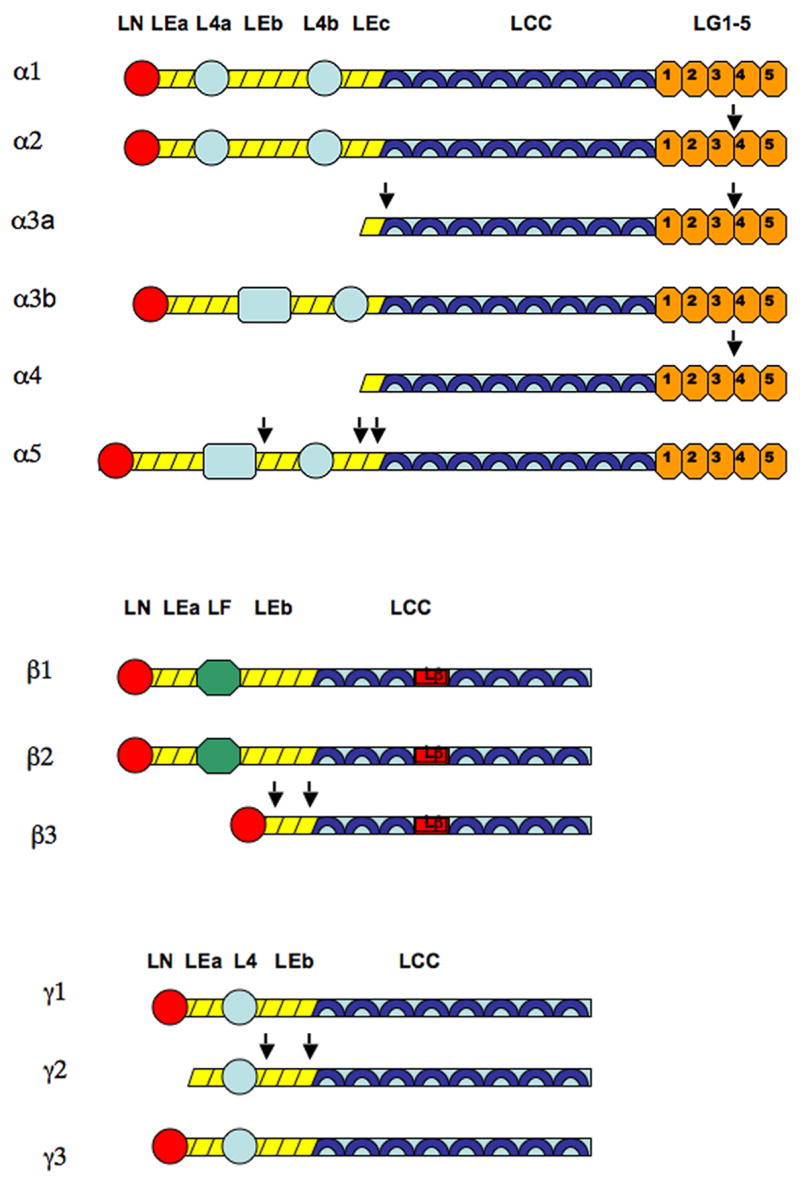
Domains of laminin alpha, beta, and gamma chains. Short arms of each chain are comprised of rodlike EGF-like tandems (LEa, LEb, LEc) and globular domains (LN, L4a, L4b, L4, LF). Long arms of each chain are comprised of alpha helical coils (LCC). Beta chains have a characteristic interruption of the coiled-coiled structure, known as the laminin β-knob domain (Lβ). Alpha chains also have a distinctive globular domain, consisting of five repeats (LG1-5), at the C terminal of the long arm (Patarroyo et al. 2002).
Laminin 332 processing occurs in alpha, beta, and gamma chains. Note that processing occurs at both N and the LG3-G4 site of the C terminals in the alpha 3A chain (Aumailley et al. 2003). The α2 and α4 chains also undergo processing at the LG3-G4 site (Talts et al. 1998; Talts et al. 2000). The α5 chain undergoes N terminal processing at multiple sites within the EGF-like domains (Bair et al. 2005). The β3 chain undergoes processing at two sites along its short arm (Nakashima et al. 2005). Processing of the γ chain occurs at two sites as well, producing an internal DIII fragment that is implicated in cell motility (Koshikawa et al. 2005; Veitch et al. 2003). Cleavage sites are indicated by arrows.
