Figure 2.
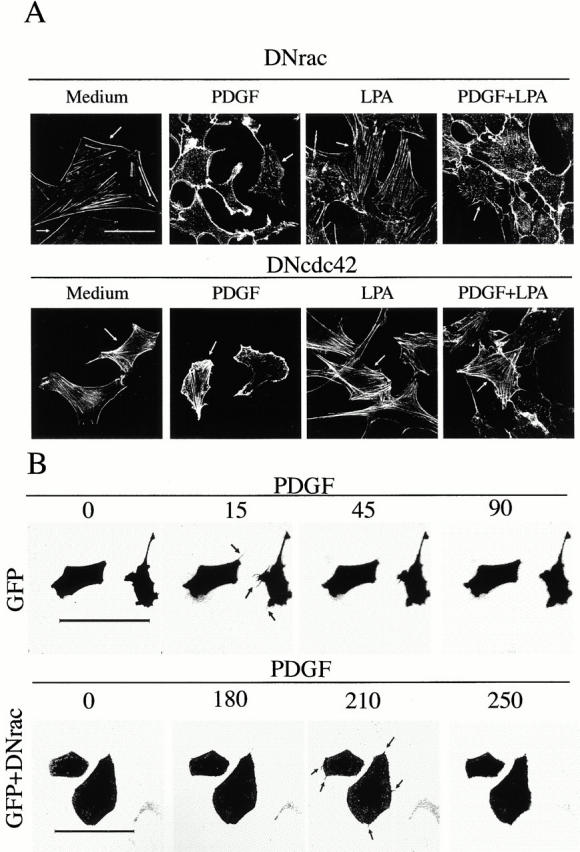
The PDGF-induced decrease in stress fibers is blocked by dominant negative mutants of Cdc42. (A) NIH-3T3 cells (2 × 105) were transfected with cDNA encoding myc-N17-Rac (DN-Rac, 5 μg) or myc-N17-Cdc42 (N17-Cdc42, 5 μg; indicated) using calcium phosphate. Transfected cells were incubated for 16 h in medium containing 10% serum to allow exogenous protein expression, and then incubated for an additional 16-h period in medium containing 0.1% serum. Cells were stimulated as in Fig. 1, fixed, and stained with FITC-phalloidin. Transfected cells (indicated by an arrow) were detected by simultaneous indirect immunofluorescence using anti-myc primary Ab. The figure illustrates that DN-Cdc42 blocks PDGF-induced stress fiber disassembly, whereas DN-Rac inhibits PDGF-induced lamellipodial extensions, enhancing detection of PDGF-induced filopodium-like structures. (B) 2 × 105 NIH-3T3 cells were transfected with cDNA encoding GFP (2.5 μg) or with cDNA encoding GFP plus cDNA encoding DN-Rac (2.5 μg each). Cells were incubated as in A, and videos were filmed before and upon addition of PDGF (50 ng/ml) with images taken every 15 s using a Leica laser confocal microscope and TCS-NT software. The figure shows selected time points after PDGF treatment. One representative experiment of five performed with similar results is shown. Bars, 100 μm.
