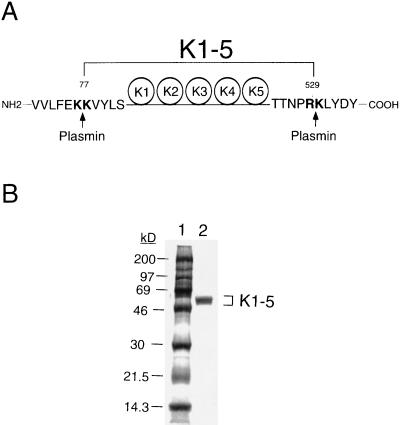
Figure 1.
Proteolytic fragment of human K1–5. (A) Plasmin cleavage sites. K1–5 fragment can be released by digestion of human Glu1-Pgn with urokinase-activated plasmin. N- and C-terminal sequencing analyses of purified K1–5 revealed that cleavage sites of plasmin were dibasic amino acids between Lys76 and Lys77 at the N terminus and between Arg529 and Lys530 at the C terminus, as indicated by arrows. K1–5 contains K1–4 and most part of K5 structures of Pgn. (B) SDS/PAGE analysis. The plasmin-digested K1–5 was purified by lysine-Sepharose affinity chromatography, followed by filtration through a Sephadex G-75 column. Four micrograms of purified protein were analyzed on a 10–20% gradient gel by SDS/PAGE under reducing conditions, followed by staining with Coomassie blue. K1–5 with molecular mass of 55 kDa was purified to homogeneity (lane 2). The molecular mass markers are indicated (in kDa) in lane 1.