Figure 1.
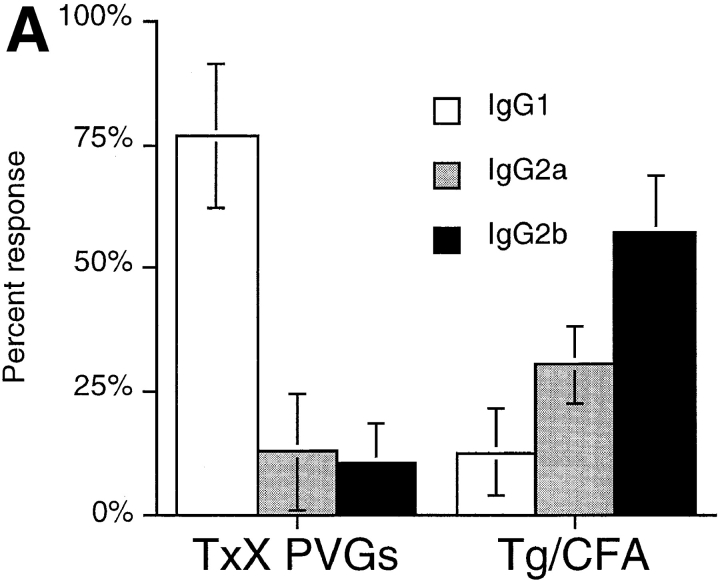
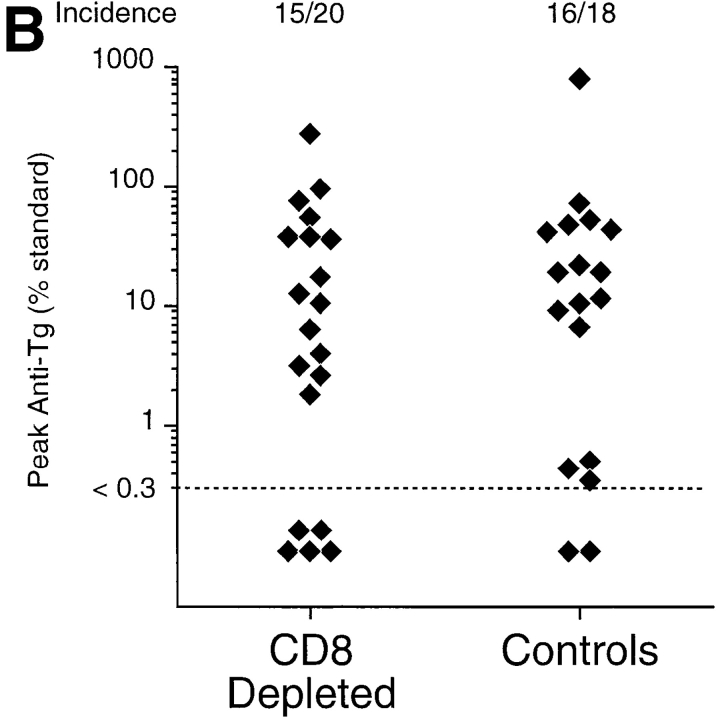
Thyroiditis in PVG rats after their thymectomy and irradiation develops independently of CD8+ cells and is characterized by a Th2-like anti-Tg IgG response. Female PVG rats were thymectomized at 3 wk of age followed 1 wk later, by four doses of 275 rad 137Cs γ-irradiation at 2-wk intervals. (A) The isotype of anti-Tg IgG antibodies in sera of TxX rats with thyroiditis (n = 25) and normal 12-wk-old female PVG rats immunized with Tg (50 μg/rat) in CFA (n = 5) was determined by specific ELISA. Data are expressed as the mean percentage of the anti-Tg response for each IgG isotype where 100% is the sum of the ODs for individual isotypes above background of normal PVG sera in 1:10 dilutions of an experimental serum. Error bars indicate SD. (B) The requirement for CD8+ cells in the development of thyroiditis in TxX PVG rats was determined by their injection at the time of thymectomy and 7 d later with either the anti-CD8-depleting mAb OX8 (0.5 mg/injection) or PBS as control. Development of anti-Tg IgG responses was monitored between 4 and 12 wk after the last irradiation by specific ELISA. Data represent peak anti-Tg IgG titers expressed as percentage of standard for individual TxX rats. FACS® analysis of splenocytes from OX8-treated rats, 12 wk after the last irradiation, showed that <2% of TCR+ cells were CD8+ (data not shown). Data are representative of two independent experiments.