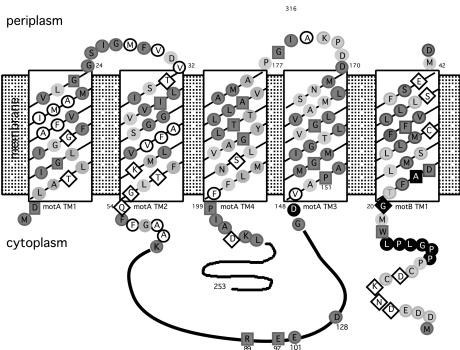
Figure 1.
Topology of MotA and MotB, showing conserved residues within the predicted transmembrane (TM) domains and sites conferring phenamil resistance. Shading denotes conservation of amino acids observed in MotA and MotB sequences from E. coli, Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Bacillus subtilis, and V. parahaemolyticus (sequences for lateral and polar Mot proteins). Darkly shaded circles indicate well conserved amino acids (consensus >3), and lightly shaded circles indicate a match of the V. parahaemolyticus residue with at least one other as identified by the clustal w program (40). Invariant residues, conserved among organisms, are designated by the dark boxes. Nonshaded amino acids circled in black are nonconserved and nonpolar, whereas those within diamonds are nonconserved and polar. Filled black symbols indicate amino acids altered in phenamil-resistant mutants.