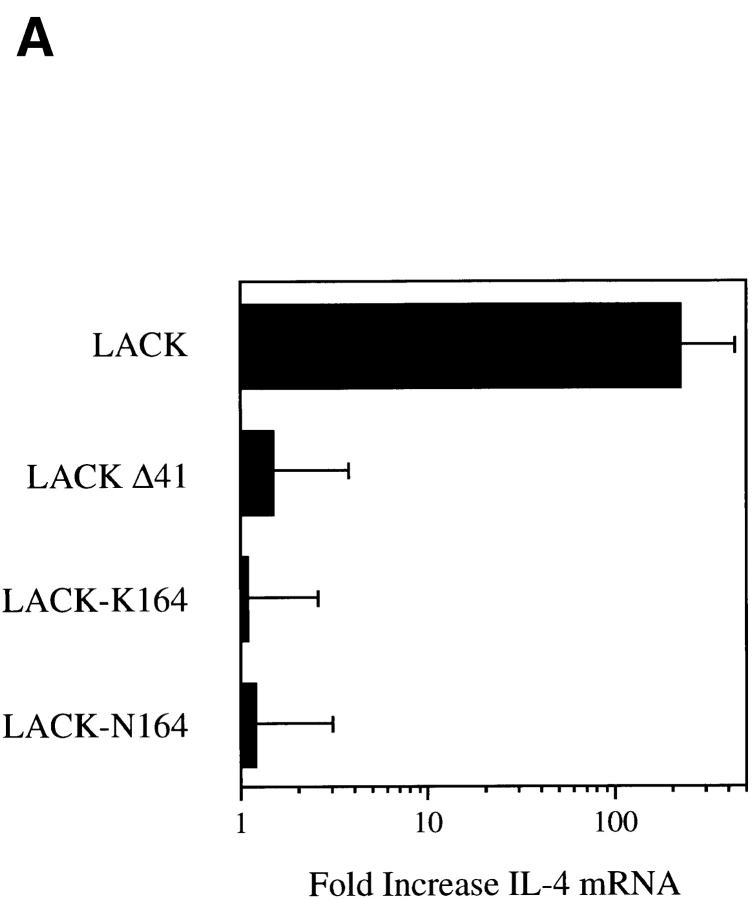
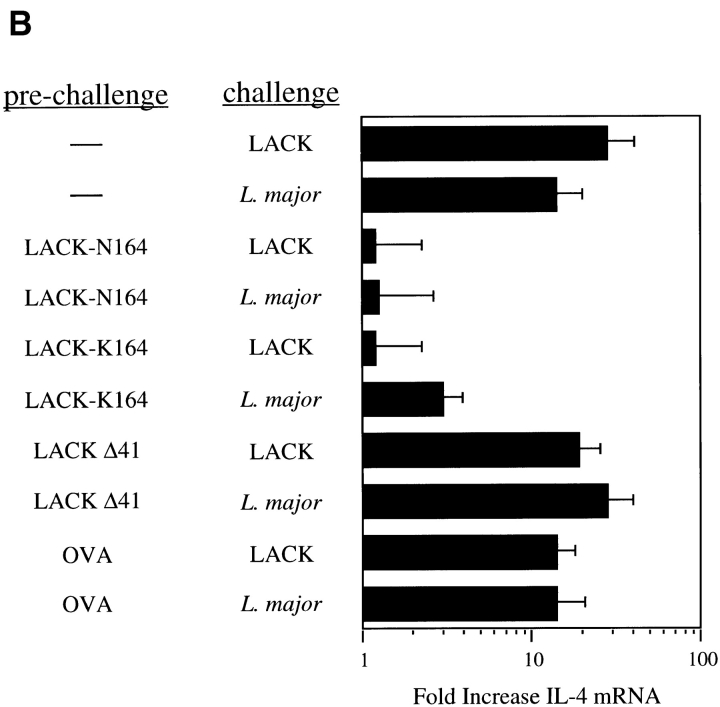
Figure 4.
LACK analogue proteins fail to activate IL-4 mRNA in vivo. (A) Popliteal lymph node cells were collected 16 h after injection of 25 μg rLACK, LACK-K164, LACK-N164, or LACKΔ41 with the I-Ad epitope deleted. RNA was purified and used to template a semiquantitative RT-PCR assay for the amounts of IL-4 transcripts. Results are expressed as the fold increase in IL-4 mRNA as compared with uninjected mice. Results shown represent comparable findings from three experiments. (B) BALB/c mice were injected in the hind footpads with 25 μg rLACK, LACK-K164, LACK-N164, LACKΔ41, or OVA (prechallenge) and then again 24 h later with either 25 μg LACK antigen or 3 × 106 L. major promastigotes (challenge). After 16 h, the popliteal lymph node cells were collected, RNA was isolated, and the relative IL-4 mRNA levels were determined using RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Results depict fold increases in IL-4 transcripts as compared with mice immunized with the same peptides but not challenged in the secondary experiment and are representative of three comparable experiments.